Overview of MTU
Definition
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) defines the maximum length of an IP packet that can be sent on an interface without fragmentation. If the length of an IP packet exceeds the MTU, the packet is fragmented before being sent out.
Application
At the data link layer, the MTU is used to limit the length of a frame. Each vendor may define different MTUs for their products or even different product models.
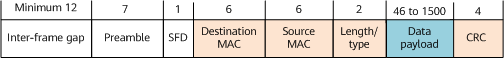
Use an Ethernet as an example. Figure 1 shows a complete Ethernet frame.
On some devices:
The MTU is configured on an Ethernet interface to indicate the maximum length of the IP packet in an Ethernet frame. Here, the MTU is an IP MTU.
- The MTU is equal to the sum of the payload, destination MAC address, source MAC address, and packet length. That is, MTU = IP MTU + 14 bytes.
- The MTU is equal to the sum of the payload, destination MAC address, source MAC address, CRC, and packet length. That is, MTU = IP MTU + 18 bytes.
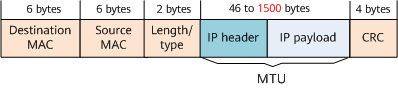
On the NetEngine 8000 F, the MTU is defined at Layer 3. As shown in Figure 2, the MTU indicates the maximum length of the IP header and payload. If the MTU of an Ethernet interface is set to 1500 bytes, packets with the maximum length of the IP header and payload less than 1500 bytes are not fragmented.
Purpose
The MTU determines the maximum number of bytes of a packet that a sender can send each time. It must be correctly set to ensure normal communication between devices.