IPv4 over IPv6 MTU Fragmentation
IPv4 over IPv6 MTU Definition
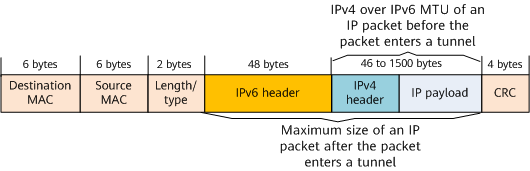
Before forwarding an IPv4 packet through an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel, a device adds an IPv6 header before the packet's IPv4 header. After the packet is encapsulated with an IPv6 header, its size may exceed the maximum size that the data link layer permits, resulting in a forwarding failure. Introducing an IPv4 over IPv6 MTU addresses this issue. An IPv4 over IPv6 MTU is the maximum size of a non-fragmented IP packet to be sent before it enters an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel. After the packet enters the tunnel, its maximum size must contain an IPv6 header, as shown in Figure 1.
IPv4 over IPv6 MTU Application Scenarios
An IPv4 over IPv6 MTU applies only to IPv4 traffic that enters an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel. Specifically, it applies to inbound tunnel traffic from an IPv4 network to an IPv6 network on a border routing device between the two networks in an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel scenario.
Effective IPv4 over IPv6 MTU Value
The effective MTU value on an IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel interface is the smaller value between the theoretical and configured IPv4 over IPv6 MTU values.
- Theoretical IPv4 over IPv6 MTU value = min (Outbound interface's IPv6 MTU value, IPv6 PMTU value) – 48 (IPv6 header)
- An IPv4 over IPv6 MTU value can be configured using the mtu command in the tunnel interface view.
Table 1 lists the parameters that affect the effective IPv4 over IPv6 MTU value.
Scenario |
Parameters That Affect the Effective IPv4 over IPv6 MTU Value (√ Indicates the Parameter That Affects the Value, and × Indicates the Parameter That Does Not Affect the Value) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
IPv4 over IPv6 |
IPv6 PMTU |
Outbound interface's IPv6 MTU |
MTU configured on a tunnel interface |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|

In an IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel scenario, packets can be fragmented during forwarding on an IPv4 network. Therefore, you can choose to configure an MTU on a tunnel interface.
- If an MTU is configured on a tunnel interface, the IPv6 over IPv4 MTU is the configured MTU.
- If no MTU is configured on a tunnel interface, the IPv6 over IPv4 MTU is the default value (1500 bytes).