Configuring Basic BIERv6 Functions
Configuring basic BIERv6 functions involves configuring sub-domains, BFR-prefixes, End.BIER SIDs, and BSLs for bit forwarding routers (BFRs). In addition, a BFR-ID needs to be configured for each bit forwarding egress router (BFER).
Context
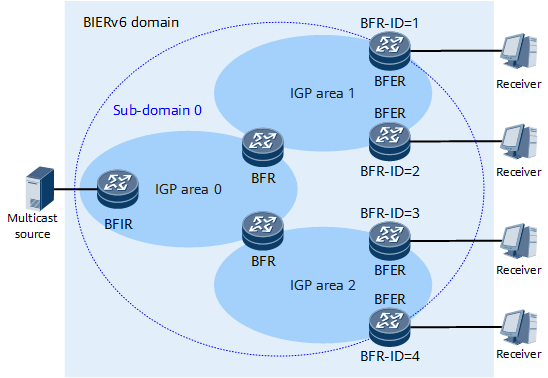
A BIERv6 network consists of one or more sub-domains. Figure 1 shows a BIERv6 network. All nodes that support BIERv6 forwarding are called BFRs. The ingress node of multicast traffic is called a bit forwarding ingress router (BFIR), and the egress node is called a BFER.
A BFR can belong to one or more sub-domains. When planning sub-domains, ensure that the BFIR and all the BFERs to which the multicast traffic received by the BFIR is to be sent reside in the same sub-domain. This is necessary because sub-domain stitching is currently not supported. To facilitate management and improve the forwarding efficiency on a multicast network, you are advised to plan sub-domains based on the suggestions provided in Table 1. A domain consists of one or more sub-domains and does not need to be configured.
Network Type |
Planning Suggestion |
|---|---|
Single-AS small- and medium-sized network |
Plan only one sub-domain, with all IGP areas in it. |
Single-AS large-scale network |
The solutions are as follows: Plan only one sub-domain, with all IGP areas in it. In addition, set BFR-IDs and BSLs to let the BFERs in the same IGP area have the same set ID. This helps improve forwarding efficiency. The concept and calculation formula of a set ID are described in the following section. |
Single-AS multi-topology network |
Plan sub-domains in one domain based on the number of topologies, with each topology corresponding to one sub-domain. |
Multi-AS large-scale network |
Inter-AS static traversal must be deployed. The sub-domain planning solutions are as follows: Plan only one sub-domain, with all ASs in it. In addition, set BFR-IDs and BSLs to let the BFERs in the same AS have the same set ID. This helps improve forwarding efficiency. The concept and calculation formula of a set ID are described in the following section. |
One BFR can be configured with one or more BSLs. The BFR-ID of a BFER in a sub-domain must be unique. Planning BSLs and BFR-IDs properly can reduce the number of multicast packet copies and improve the forwarding efficiency on the multicast network. When planning BSLs and BFR-IDs, you are advised to adhere to the following guidelines:
- Denseness: Set the maximum BFR-ID as the number of BFERs in a sub-domain to deploy as few sets as possible. For example, if a sub-domain contains up to 256 BFERs, allocate BFR-IDs to the BFERs within the range of 1 to 256. Similarly, if the sub-domain contains up to 512 BFERs, allocate BFR-IDs to the BFERs within the range of 1 to 512.
- Uniqueness: Ensure that each BFR-ID is unique in a sub-domain.
- Region: Allocate the BFERs in the same region to the same set.
- Necessity: Allocate BFR-IDs only for BFERs. If a BFIR also needs to function as a BFER, you also need to configure a BFR-ID for it. For a BFIR-only node (functioning as a BFIR but not a BFER), it does not need to be configured with a BFR-ID.
- Evolvability: Reserve some BFR-IDs in each set for future network expansion.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Enable SRv6 and configure a locator address.
If SRv6 has been enabled and an SRv6 locator has been configured for the local device, skip this step. Otherwise, perform the following operations:
- Configure an IPv6 address (to be used as the BFR-prefix) for an interface.
A BFR-prefix is a loopback interface IPv6 address of the BFR in a sub-domain. If an IPv6 address has been configured for the interface on the local device, skip this step; otherwise, perform the following operations:
- Run bier
BIER is enabled, and the BIER view is displayed.
- Run sub-domain sub-domain-val ipv6
A sub-domain is specified for the BFR, and the sub-domain view is displayed.
- Configure BIERv6-related attributes.
Table 2 describes these attributes.
Table 2 BIERv6-related attributes Operation
Command
Remarks
Configure a BFR-ID for the BFER.
bfr-id bfr-id-val
This operation is not required for non-BFER nodes. If a BFIR also needs to function as a BFER, you also need to configure a BFR-ID for it.
On an MVPN over BIERv6 network, all receiver PEs are BFERs.
Set the BSL and Max-SI.
encapsulation-type ipv6 bsl { 64 | 128 | 256 } max-si max-si-val
Max-SI is the maximum set ID in a sub-domain. The formula for calculating the set ID is as follows:
Set ID = int [ (BFR-ID – 1)/BSL ]
In the preceding formula, int rounds down to the nearest integer.
Specify the interface whose IP address is to be used as the BFR-prefix.
bfr-prefix interface { interface-name | interface-type interface-number } [ ipv6-address-value ]
A loopback interface must be specified, and IS-IS IPv6 must be enabled on the interface.
Configure an End.BIER SID.
end-bier locator locator-name sid ipv6-sid
The End.BIER SID must be an IPv6 address of the subnet to which the locator belongs.
Configure the underlay protocol to be used to advertise BIERv6 information.
protocol isis
Currently, IS-IS or a static BIFT can be used to advertise BIERv6 information. The latter is used in inter-AS static traversal scenarios.
(Optional) Configure the maximum number of links for load balancing.
max-load-balance max-load-balance-num
Perform this operation only when BIERv6 link load balancing is required.
- Run quit
Exit the sub-domain view.
- Run quit
Exit the BIER view.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Repeat 1 to 9 to configure all other BFRs on the BIERv6 network.