Example for Configuring DSVPN in Shortcut Mode (BGP)
Networking Requirements
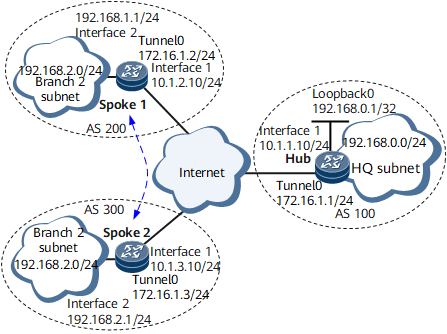
In a large enterprise, the HQ hub connects to branch spokes over the public network, and Spoke 1 and Spoke 2 also connect over the public network. Spokes use dynamic IP addresses to connect to the public network. The HQ hub and branch spokes are located in different areas and belong to different ASs, and the subnet environments of the HQ and branches change frequently. The enterprise wants to use a VPN for communication between branch spokes. To meet this requirement, configure dynamic routing (OSPF) for intra-AS routing and EBGP for inter-AS routing based on the enterprise network planning and deploy DSVPN in shortcut mode to realize direct communication between Spoke 1 and Spoke 2. Figure 1 shows the related networking.
Configuration Roadmap
Because branches access the public network through dynamic IP addresses, branches are unaware of each other's public IP address. Therefore, configure DSVPN to interconnect branches.
Because a large number of branches exist, configure DSVPN in shortcut mode.
Because the subnet environments of the HQ and branches frequently change, deploy BGP based on enterprise network planning for communication between the HQ and branches to simplify maintenance.
Procedure
- Configure interface IP addresses.
Configure interface IP addresses on each device.
# Configure interface IP addresses on Hub.<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname Hub [*Hub] commit [~Hub] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*Hub-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.0 [*Hub-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] binding tunnel gre [*Hub-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*Hub] interface tunnel 0 [*Hub-Tunnel0] ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 [*Hub-Tunnel0] quit [*Hub] interface loopback 0 [*Hub-LoopBack0] ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.255 [*Hub-LoopBack0] quit [*Hub] commit
Assign an IP address to each interface on Spoke 1 and Spoke 2 according to Figure 1. The configurations of the spokes are similar to the configuration of the hub.
- Configure public network routes between devices to implement connectivity.
Configure OSPF on each device to ensure that the public network routes are available.
# Configure OSPF on Hub.
[~Hub] ospf 2 router-id 10.1.1.10 [*Hub-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.1 [*Hub-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*Hub-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] quit [*Hub-ospf-2] quit [*Hub] commit
# Configure OSPF on Spoke 1.
[~Spoke1] ospf 2 router-id 10.1.2.10 [*Spoke1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.1 [*Spoke1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*Spoke1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] quit [*Spoke1-ospf-2] quit [*Spoke1] commit
# Configure OSPF on Spoke 2.
[~Spoke2] ospf 2 router-id 10.1.3.10 [*Spoke2-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.1 [*Spoke2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 [*Spoke2-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.1] quit [*Spoke2-ospf-2] quit [*Spoke2] commit
- Configure routes in ASs.
Configure OSPF on the hub and spokes in different ASs to implement reachability in ASs.
# Configure Hub.
[~Hub] ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.1 [*Hub-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [*Hub-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 [*Hub-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*Hub-ospf-1] quit [*Hub] commit
# Configure Spoke 1.
[~Spoke1] ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.2 [*Spoke1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [*Spoke1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*Spoke1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*Spoke1-ospf-1] quit [*Spoke1] commit
# Configure Spoke 2.
[~Spoke2] ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.3 [*Spoke2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0 [*Spoke2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 [*Spoke2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*Spoke2-ospf-1] quit [*Spoke2] commit

The configuration of one branch subnet is used as an example. Perform the same configuration on other branch subnets.
If a branch subnet is changed, you only need to configure the corresponding dynamic routing attribute on the local device.
- Configure basic EBGP functions.
# Configure Hub.
[~Hub] bgp 100 [*Hub-bgp] router-id 172.16.1.1 [*Hub-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*Hub-bgp] peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 200 [*Hub-bgp] peer 172.16.1.3 as-number 300 [*Hub-bgp] aggregate 192.168.0.0 16 detail-suppressed [*Hub-bgp] quit [*Hub] commit

During configuration of route summarization, the summarized address must exist. Therefore, configure the loopback interface address as the summarized address.
# Configure Spoke 1.
[~Spoke1] bgp 200 [*Spoke1-bgp] router-id 172.16.1.2 [*Spoke1-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*Spoke1-bgp] peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 100 [*Spoke1-bgp] quit [*Spoke1] commit
# Configure Spoke 2.
[~Spoke2] bgp 300 [*Spoke2-bgp] router-id 172.16.1.3 [*Spoke2-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*Spoke2-bgp] peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 100 [*Spoke2-bgp] quit [*Spoke2] commit
- Enable NHRP globally.
# Configure Hub.
[~Hub] nhrp enableThe configurations of the spokes are similar to the configuration of the hub. For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
- Configure tunnel interfaces.Configure route attributes on the hub and spokes to implement routing from the spokes to the hub. Enable NHRP redirect on Hub. Configure the Hub's static NHRP peer entries and enable the NHRP shortcut function on Spoke 1 and Spoke 2.

Configure BGP when the shortcut mode is used. The related attributes are configured in the BGP view.
# Configure a tunnel interface and enable NHRP redirect on Hub.[~Hub] interface tunnel 0 [*Hub-Tunnel0] tunnel-protocol gre p2mp [*Hub-Tunnel0] nhrp enable [*Hub-Tunnel0] source gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*Hub-Tunnel0] nhrp entry multicast dynamic [*Hub-Tunnel0] nhrp redirect [*Hub-Tunnel0] quit [*Hub] commit
# Configure a tunnel interface and the Hub's static NHRP peer entry, and enable NHRP shortcut on Spoke 1.[~Spoke1] interface tunnel 0 [*Spoke1-Tunnel0] tunnel-protocol gre p2mp [*Spoke1-Tunnel0] nhrp enable [*Spoke1-Tunnel0] source gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*Spoke1-Tunnel0] nhrp entry 172.16.1.1 10.1.1.10 register [*Spoke1-Tunnel0] nhrp shortcut [*Spoke1-Tunnel0] quit [*Spoke1] commit
# Configure a tunnel interface and the Hub's static NHRP peer entry, and enable NHRP shortcut on Spoke 2.[~Spoke2] interface tunnel 0 [*Spoke2-Tunnel0] tunnel-protocol gre p2mp [*Spoke2-Tunnel0] nhrp enable [*Spoke2-Tunnel0] source gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*Spoke2-Tunnel0] nhrp entry 172.16.1.1 10.1.1.10 register [*Spoke2-Tunnel0] nhrp shortcut [*Spoke2-Tunnel0] quit [*Spoke2] commit
- Verify the DSVPN configuration.
After completing the configuration, verify the NHRP peer entry on spokes.
# Run the display nhrp peer all command on Spoke 1. The command output is as follows.[~Spoke1] display nhrp peer all ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.1 32 10.1.1.10 172.16.1.1 hub up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:10:58 Expire time : -- Number of nhrp peers: 1# Run the display nhrp peer all command on Spoke 2. The command output is as follows.[~Spoke2] display nhrp peer all ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.1 32 10.1.1.10 172.16.1.1 hub up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:07:55 Expire time : -- Number of nhrp peers: 1
The display nhrp peer all command output shows that the static NHRP peer entry mapped only to Hub is displayed on Spoke 1 and Spoke 2.
On Hub, verify registration information about Spoke 1 and Spoke 2.
# Run the display nhrp peer all command on Hub. The command output is as follows.[~Hub] display nhrp peer all ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.2 32 10.1.2.10 172.16.1.2 registered up|unique ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:02:02 Expire time : 01:57:58 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.3 32 10.1.3.10 172.16.1.3 registered up|unique ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:01:53 Expire time : 01:59:35 Number of nhrp peers: 2 - Run the ping command and check the configuration result.
On Spoke 1, ping the subnet address 192.168.2.1 of Spoke 2. Then, verify the dynamic NHRP peer entries of Spoke 1 and Spoke 2.
# Run the ping -a 192.168.1.1 192.168.2.1 command on Spoke 1. The ping is successful.
[~Spoke1] ping -a 192.168.1.1 192.168.2.1 PING 192.168.2.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=3 ms Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=2 ms Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=2 ms Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=2 ms Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=2 ms --- 192.168.2.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/3 ms# Run the display nhrp peer all command on Spoke 1. The command output is as follows.
[~Spoke1] display nhrp peer all ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.1 32 10.1.1.10 172.16.1.1 hub up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:46:35 Expire time : -- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 192.168.2.1 32 10.1.3.10 172.16.1.3 remote-network up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:00:28 Expire time : 01:59:32 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.3 32 10.1.3.10 172.16.1.3 remote up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:00:28 Expire time : 01:59:32 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.2 32 10.1.2.10 172.16.1.2 local up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:00:28 Expire time : 01:59:32 Number of nhrp peers: 4# Run the display nhrp peer all command on Spoke 2. The command output is as follows.
[~Spoke2] display nhrp peer all ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.1 32 10.1.1.10 172.16.1.1 hub up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:43:32 Expire time : -- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 192.168.1.1 32 10.1.2.10 172.16.1.2 remote-network up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:00:47 Expire time : 01:59:13 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.2 32 10.1.2.10 172.16.1.2 remote up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:00:47 Expire time : 01:59:13 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Protocol-addr Mask NBMA-addr NextHop-addr Type Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 172.16.1.3 32 10.1.3.10 172.16.1.3 local up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Tunnel interface: Tunnel0 (VPN instance: _public_) Created time : 00:00:47 Expire time : 01:59:13 Number of nhrp peers: 4
Configuration Files
Hub configuration file
# sysname Hub # nhrp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.0 binding tunnel gre # interface LoopBack0 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.255 # interface Tunnel0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 tunnel-protocol gre p2mp source GigabitEthernet0/1/0 nhrp enable nhrp redirect nhrp entry multicast dynamic # bgp 100 router-id 172.16.1.1 peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 200 peer 172.16.1.3 as-number 300 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization aggregate 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 detail-suppressed import-route ospf 1 peer 172.16.1.2 enable peer 172.16.1.3 enable # ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf 2 router-id 10.1.1.10 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Spoke 1 configuration file
# sysname Spoke1 # nhrp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.2.10 255.255.255.0 binding tunnel gre # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface Tunnel0 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 tunnel-protocol gre p2mp source GigabitEthernet0/1/0 nhrp enable nhrp shortcut nhrp entry 172.16.1.1 10.1.1.10 register # bgp 200 router-id 172.16.1.2 peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospf 1 peer 172.16.1.1 enable # ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.2 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf 2 router-id 10.1.2.10 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Spoke 2 configuration file
# sysname Spoke2 # nhrp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.3.10 255.255.255.0 binding tunnel gre # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface Tunnel0 ip address 172.16.1.3 255.255.255.0 tunnel-protocol gre p2mp source GigabitEthernet0/1/0 nhrp enable nhrp shortcut nhrp entry 172.16.1.1 10.1.1.10 register # bgp 300 router-id 172.16.1.3 peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospf 1 peer 172.16.1.1 enable # ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.3 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf 2 router-id 10.1.3.10 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return