Example for Configuring a 6RD Relay
This section provides an example for configuring a 6RD relay to allow the hosts or devices on an isolated IPv6 network and in a 6RD domain to communicate with each other.
Networking Requirements
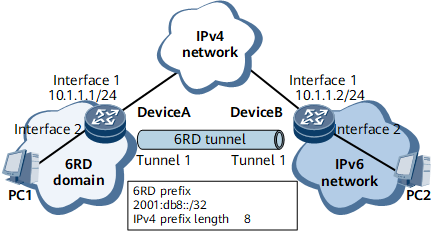
As shown in Figure 1, both DeviceA and DeviceB support the IPv4/IPv6 dual stack and are connected to an IPv6 network and an IPv4 network. DeviceA functions as a 6RD CE and is connected to an IPv6 6RD network. DeviceB functions as a 6RD BR and is connected to a common IPv6 network outside the 6RD domain. A 6RD tunnel needs to be established between DeviceA and DeviceB so that the hosts on the two IPv6 networks can communicate with one another.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
On DeviceA and DeviceB, configure IPv4 addresses for the physical interfaces connected to the IPv4 network and enable IPv6 packet forwarding.
On DeviceA and DeviceB, configure the source IPv4 address, 6RD prefix, IPv6 prefix length, and IPv4 prefix length for a 6RD tunnel. Then calculate the 6RD delegated prefix based on a combination of these parameters.
On DeviceA and DeviceB, configure IPv6 addresses for the physical interfaces connected to the 6RD domain and IPv6 network based on the 6RD delegated prefix.
Configure the IPv6 addresses on PC1 and PC2 and set the IPv6 prefix of PC1 to a 64-bit address prefix that contains the 6RD prefix and subnet ID and the IPv6 prefix of PC2 to a common IPv6 address prefix.
On DeviceA, configure a static route destined for the IPv6 network on which DeviceB resides. On DeviceB, configure a static route destined for the 6RD domain in which DeviceA resides.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IPv4 addresses of interfaces
Source IPv4 address of a 6RD tunnel interface
6RD prefix and length of a 6RD tunnel
IPv4 prefix length of a 6RD tunnel
Procedure
- Configure IPv4 addresses for interfaces that connect devices to the IPv4 network.
# Configure DeviceA.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceA [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
# Configure DeviceB.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceB [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Configure a 6RD tunnel.
# Configure DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] interface Tunnel 1 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol ipv6-ipv4 6rd [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] ipv6 enable [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] source GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] ipv6-prefix 2001:db8::/32 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] ipv4-prefix length 8 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] border-relay address 10.1.1.2 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] commit
# Configure DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] interface Tunnel 1 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol ipv6-ipv4 6rd [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] ipv6 enable [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] source GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] ipv6-prefix 2001:db8::/32 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] ipv4-prefix length 8 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] commit

The 6RD delegated prefix can be automatically calculated based on the configured source tunnel address or source interface, 6RD prefix, IPv6 prefix length, and IPv4 prefix length. You can run the display this interface command to view the 6RD delegated prefix and then configure an IPv6 address for the tunnel interface.
- Query the calculated 6RD delegated prefix.
# Display the calculated 6RD delegated prefix on DeviceA.
[~DeviceA-Tunnel1] display this interface Tunnel1 current state : UP (ifindex: 9) Line protocol current state : DOWN Description: Route Port,The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500 Internet protocol processing : disabled Encapsulation is TUNNEL, loopback not set Tunnel source 10.1.1.1, destination unknown Tunnel protocol/transport IPv6 over IPv4 (6rd) ipv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/32 ipv4 prefix length 8 6RD Operational, Delegated Prefix is 2001:DB8:101:100::/56 Current system time: 2017-09-02 10:14:49 300 seconds input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 300 seconds output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 seconds input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 seconds output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 packets input, 0 bytes 0 input error 0 packets output, 0 bytes 0 output error Input: Unicast: 0 packets, Multicast: 0 packets Output: Unicast: 0 packets, Multicast: 0 packets Last 300 seconds input utility rate: -- Last 300 seconds output utility rate: --
# Display the calculated 6RD delegated prefix on DeviceB.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] display this interface Tunnel1 current state : UP (ifindex: 10) Line protocol current state : DOWN Description: Route Port,The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500 Internet protocol processing : disabled Encapsulation is TUNNEL, loopback not set Tunnel source 10.1.1.2, destination unknown Tunnel protocol/transport IPv6 over IPv4 (6rd) ipv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/32 ipv4 prefix length 8 6RD Operational, Delegated Prefix is 2001:db8:101:200::/56 Current system time: 2017-09-02 10:22:13 300 seconds input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 300 seconds output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 seconds input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 seconds output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 packets input, 0 bytes 0 input error 0 packets output, 0 bytes 0 output error Input: Unicast: 0 packets, Multicast: 0 packets Output: Unicast: 0 packets, Multicast: 0 packets Last 300 seconds input utility rate: -- Last 300 seconds output utility rate: -- - Configure IPv6 addresses for the tunnel interfaces based on the 6RD delegated prefix.
# Configure DeviceA.
[~DeviceA-Tunnel1] ipv6 address 2001:db8:101:100::1 56 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] commit [~DeviceA-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure DeviceB.
[~DeviceB-Tunnel1] ipv6 address 2001:db8:101:200::1 56 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] commit [~DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit
- Configure an IPv6 address for GE 0/1/2 on each Device.
# Configure DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ipv6 enable [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ipv6 address 2001:db8:101:101::1 64 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
# Configure DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ipv6 enable [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ipv6 address 2001:db8::1 64 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
- Configure static routes.
# Configure a static route destined for the IPv6 network connected to DeviceB.
[~DeviceA] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:: 32 Tunnel 1 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure a static route destined for the 6RD domain connected to DeviceA.
[~DeviceB] ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:: 32 Tunnel 1 [*DeviceB] commit
- Configure IPv6 addresses for PC1 and PC2.
# Configure PC1.
Configure the IPv6 address 2001:db8:101:101::2/64 for PC1 based on the 6RD delegated prefix. The PC1's IPv6 address must be on the same network segment as GE 0/1/2 of DeviceA. Configure a static route from PC1 to DeviceA and set the destination address to 2001:db8:: 32. The method of configuring the IPv6 address and static route is related to the operating system running on PC1. The configuration details are not provided.
# Configure PC2.
Configure the IPv6 address 2002:db8::2/64 for PC2 based on the 6RD delegated prefix. The PC2's IPv6 address must be on the same network segment as GE 0/1/2 of DeviceB. Configure a static route 2001:db8:: 32 from PC2 to DeviceB. The method of configuring the IPv6 address and static route is related to the operating system running on PC2. The configuration details are not provided.
- Verify the configuration.
# After completing the configuration, check the IPv6 status of Tunnel 1 on DeviceA or DeviceB. The following command output shows that the IPv6 status of Tunnel 1 is UP.
[~DeviceA] display ipv6 interface Tunnel 1 Tunnel1 current state : UP IPv6 protocol current state : UP IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::3ABA:9A00:9DC:D303 Global unicast address(es): 2001:DB8:101:100::1, subnet is 2001:DB8:101:100::/56 Joined group address(es): FF02::1:FF00:1 FF02::1:FFDC:D303 FF02::2 FF02::1 MTU is 1500 bytes ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1 ND reachable time is 1200000 milliseconds ND retransmit interval is 1000 milliseconds Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses
# On DeviceA, ping the IPv6 address of GE 0/1/2 on DeviceB. The following command output shows that the ping is successful.
[~DeviceA] ping ipv6 2001:db8::1 PING 2001:db8::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 2001:db8::1 bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=64 time = 4 ms Reply from 2001:db8::1 bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=64 time = 3 ms Reply from 2001:db8::1 bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=64 time = 2 ms Reply from 2001:db8::1 bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=64 time = 2 ms Reply from 2001:db8::1 bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=64 time = 2 ms --- 2001:db8::1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/4 ms
# On PC1, ping the IPv6 address of PC2. The following command output shows that the ping is successful.
C:\> ping 2001:db8::2 Pinging 2001:db8::2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 2001:db8::2: time<1ms Reply from 2001:db8::2: time<1ms Reply from 2001:db8::2: time<1ms Reply from 2001:db8::2: time<1ms Ping statistics for 2001:db8::2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:101:101::1 64 # interface Tunnel 1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:101:100::1 56 tunnel-protocol ipv6-ipv4 6rd source GigabitEthernet0/1/1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8::/32 ipv4-prefix length 8 border-relay address 10.1.1.2 # ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:: 32 Tunnel1 # return
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8::1 64 # interface Tunnel 1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:101:200::1 56 tunnel-protocol ipv6-ipv4 6rd source GigabitEthernet0/1/1 ipv6-prefix 2001:db8::/32 ipv4-prefix length 8 # ipv6 route-static 2001:db8:: 32 Tunnel1 # return