Overview of Accessing Other Devices
You can log in to one device and access another device using Telnet, FTP, TFTP or SFTP.
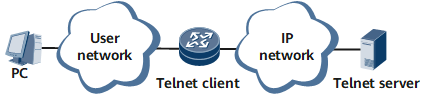
As shown in Figure 1, after you use the terminal emulator or Telnet program on a PC to connect to the router, you can use Telnet, FTP, TFTP or SFTP to access other devices from the router functioning as a client.
Telnet
Telnet is an application layer protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite and provides remote login and virtual terminal services. The NetEngine 8000 F provides the following Telnet services:
Telnet server: A user runs the Telnet client program on a PC to log in to the device to configure and manage the device. The device functions as a Telnet server.
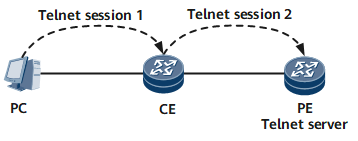
Telnet client: After using the terminal emulator or Telnet client program on a PC to connect to the device, a user runs the telnet command to log in to another device for configuration and management. The device functions as a Telnet client. In Figure 2, the CE functions as both a Telnet server and a Telnet client.
-
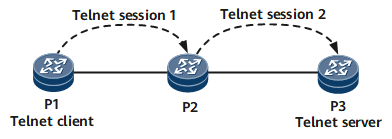
Two types of shortcut keys can be used to interrupt Telnet connections. As shown in Figure 3, P1 uses Telnet to log in to P2 and then to P3. P1 is the Telnet client of P2, and P2 is the Telnet client of P3. The usage of shortcut keys is described as follows:
Ctrl_]: Instructs the server to disconnect a Telnet connection.
When the network works properly, entering the shortcut key Ctrl_] causes the Telnet server to interrupt the current Telnet connection.
For example, after you enter Ctrl_] on P3, the <P2> prompt is displayed.
<P3> Select Ctrl_] to return to the prompt of P2 The connection was closed by the remote host. <P2>
After you enter Ctrl_] on P2, the <P1> prompt is displayed.
<P2> Ctrl_] The connection was closed by the remote host. <P1>

If the network connection is disconnected, shortcut keys do not take effect.
Ctrl_K: Instructs the client to disconnect the connection.
When the server fails and the client is unaware of the failure, the server does not respond to the client's input. If you enter Ctrl_K, the Telnet client interrupts and quits the Telnet connection.
For example, enter Ctrl_K on P3 to quit the Telnet connection.
<P3> Ctrl_K <P1>

When the number of remote login users reaches the maximum number of VTY user interfaces, the system prompts subsequent users with a message, indicating that all user interfaces are in use and no more Telnet connections are allowed.
FTP
- Control connection: issues commands from the client to the server and transmits replies from the server to the client, minimizing the transmission delay.
- Data connection: transmits data between the client and server, maximizing the throughput.
- Binary mode: is used to transfer program files, such as .app, .bin, and .btm files.
- ASCII mode: is used to transfer text files, such as .txt, .bat, and .cfg files.
- FTP client: Users can use the terminal emulator or the Telnet program to connect PCs to the device, and run the ftp command to establish a connection between the device and a remote FTP server to access and operate files on the server.
FTP server: Users can use the FTP client program to log in to the device and operate files on the device.
Before users log in, the network administrator must configure an IP address for the FTP server.
TFTP
TFTP is an application protocol based on User Datagram Protocol (UDP) connections. It uses the UDP port number 69 to transfer files between local hosts and remote servers. Unlike FTP, TFTP is simple, providing no authentication. It is applicable to scenarios where complicated interactions between clients and the server are not required.
TFTP supports both binary and ASCII file transfer modes, which are also supported by FTP.

- Currently, the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series supports only the binary mode for TFTP.
- Currently, the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series can function only as a TFTP client but not a TFTP server.
- When a TFTP client needs to download files from the server, the client sends a read request to the TFTP server. The server sends data packets to the client, and the client acknowledges the data packets.
- When a TFTP client needs to upload a file to the server, the client sends a write request and then data to the server, and receives acknowledgments from the server.
SFTP
SFTP uses SSH to ensure secure file transfer. On one hand, SFTP allows remote users to securely log in to the device to manage and transfer files. On the other hand, users can use the device functioning as a client to log in to a remote server and transfer files securely.
- If the client does not receive any packet within the specified period, the client sends a Keepalive packet to the server.
- If the maximum number of times that the server does not respond exceeds the specified value, the client proactively releases the connection.