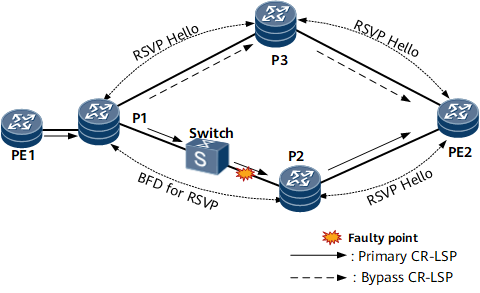
BFD for RSVP
When a Layer 2 device exists on a link between two RSVP nodes, BFD for RSVP can be configured to rapidly detect a fault in the link between the Layer 2 device and an RSVP node. If a link fault occurs, BFD for RSVP detects the fault and sends a notification to trigger TE FRR switching.
Background
Implementation
BFD for RSVP monitors RSVP neighbor relationships.
Unlike BFD for CR-LSP and BFD for TE that support multi-hop BFD sessions, BFD for RSVP establishes only single-hop BFD sessions between RSVP nodes to monitor the network layer.
BFD for RSVP, BFD for OSPF, BFD for IS-IS, and BFD for BGP can share a BFD session. When protocol-specific BFD parameters are set for a BFD session shared by RSVP and other protocols, the smallest values take effect. The parameters include the minimum intervals at which BFD packets are sent, minimum intervals at which BFD packets are received, and local detection multipliers.
Usage Scenario
BFD for RSVP applies to a network on which a Layer 2 device exists between the TE FRR point of local repair (PLR) on a bypass CR-LSP and an RSVP node on the primary CR-LSP.
Benefits
BFD for RSVP improves reliability on MPLS TE networks with Layer 2 devices.