Configuring BGP to Generate Locator Routes
Configuring BGP to generate locator routes allows different services distinguished through locators to be forwarded over different networks.
Usage Scenario
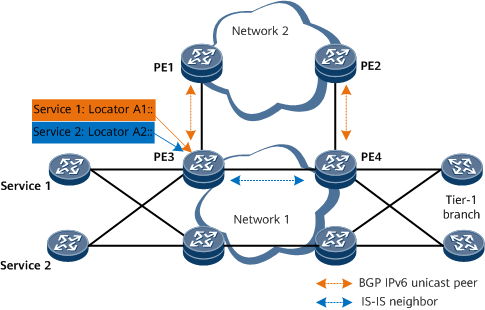
As shown in Figure 1, user services are transmitted over network 1 and network 2. Network 1 is a user-built network, and network 2 is a carrier network. An IS-IS neighbor relationship is established between PE3 and PE4. A BGP IPv6 unicast peer relationship is established between PE1 and PE3, and between PE2 and PE4. Service 1 and service 2 on the user network are distinguished through locators. To ensure that service 1 and service 2 are forwarded over different networks, you can configure this function on PE3. Suppose that locator A1:: is allocated to service 1 and that locator A2:: is allocated to service 2. Locator A1:: is advertised to PE4 through the IS-IS neighbor relationship, whereas locator A2:: is advertised to PE1 through a BGP IPv6 peer relationship and then to the tier-1 branch over network 2. In this case, the service traffic matching locator A1:: is forwarded over network 1, whereas the service traffic matching locator A2:: is forwarded over network 2.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bgp as-number
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run ipv6-family unicast
The BGP-IPv6 unicast address family view is displayed.
- Run segment-routing ipv6 generate-route locator locator-name [ route-policy policy-name | route-filter route-filter-name ]
BGP is configured to generate locator routes.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Verifying the Configuration
After configuring the function, verify the configuration.
Run the display bgp ipv6 routing-table ipv6-address command to check routes in the BGP4+ routing table.