Configuring Path MTU Auto Discovery
Path MTU auto discovery allows BGP to discover the smallest MTU value on a path so that BGP messages are transmitted based on the path MTU. This function improves transmission efficiency and BGP performance.
Usage Scenario
The link-layer MTUs of different networks that a communication path traverses may vary. The smallest MTU on the path is the most important factor that influences the communication between the two ends of the path. The smallest MTU on the communication path is called the path MTU.
The path MTU varies with the selected path and therefore may change. In addition, the path MTU in one direction may be inconsistent with that in the reverse direction. Enabling path MTU auto discovery allows a device to discover the path MTU from the transmit end to the receive end. TCP encapsulates IP packets based on the path MTU when transmitting BGP messages.
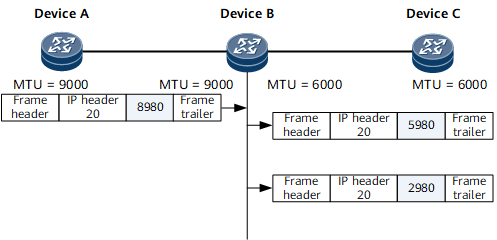
In Figure 1, path MTU auto discovery is not enabled, and a BGP peer relationship is established between Device A and Device C. After Device A sends 9000-byte BGP messages to Device C, Device B fragments the messages upon reception by encapsulating one IP header, one Layer 2 frame header, and one Layer 2 frame trailer in each fragment, which reduces transmission efficiency. If a fragment of a message is lost, the message becomes invalid.
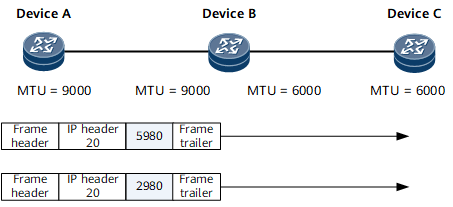
In Figure 2, path MTU auto discovery is enabled, and a BGP peer relationship is established between Device A and Device C. Device A sends BGP messages to Device C based on the path MTU (6000 bytes). In this example, Device A sends a 6000-byte BGP message and a 3000-byte BGP message. In this case, Device B does not fragment the messages upon reception, which improves transmission efficiency.

- If path MTU auto discovery is not enabled:
- After path MTU auto discovery is enabled:
On the sending end, the local MSS value is updated only when the device sends packets in which the MSS value is greater than the path MTU. The calculation formula of TCP MSS is as follows: .
-
If the device supports SYNCOOKIE, the calculation formula of TCP MSS is as follows: .
If the device does not support SYNCOOKIE, the calculation formula of TCO MSS is as follows: .
- CFGMSS: MIN { APPMSS, CLICFGMSS }
- APPMSS: Specifies the MSS configured using the peer tcp-mss command.
- CLICFGMSS: Specifies the maximum MSS configured using the tcp max-mss mss-value command.
- MTU-40: Specifies the interface MTU minus 40.
- PMTU-40: Specifies the path MTU minus 40.
- internally-defined MSS value: Specifies an internally-defined MSS value, which can be 216, 460, 952, 1400, 2900, 4900, 7900, or 9500. Upon receipt of a packet, the receive-end device uses the internally-defined MSS which is smaller than but close to the MSS of the received packet.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bgp as-number
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run peer { group-name | ipv4-address } path-mtu auto-discovery
Path MTU auto discovery is enabled.
After the command is run, a BGP peer learns the path MTU, preventing BGP messages from being fragmented during transmission.

A BGP message from one end to the other may travel a path different from the path used by the ACK message that is responded by the other end. Therefore, running this command on both ends is recommended so that both peers exchange messages based on the path MTU.
- Run quit
Return to the system view.
- Run tcp timer pathmtu-age age-time
The aging time is set for an IPv4 path MTU.
The path MTUs vary with the path. If there are multiple routes between two communication hosts and the routes selected for packet transmission change frequently, configure the path MTU aging time so that the system updates path MTUs based on the path MTU aging time, increasing the transmission efficiency.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Checking the Configurations
After configuring path MTU auto discovery, run the following commands to check the previous configuration.
- Run the display bgp peer [ ipv4-address ] verbose command to check whether path MTU auto discovery has been successfully configured.