Configuring BGP Best-external
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Best-external can speed up route convergence if the primary link fails.
Usage Scenario
If multiple routes to the same destination are available, a BGP device selects one optimal route based on BGP route selection policies and advertises the route to its BGP peers. This optimal route may be advertised by either an External Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP) peer or an Internal Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP) peer.
However, in scenarios with master and backup provider edges (PEs), if routes are selected based on the preceding policies and the primary link fails, the BGP route convergence takes a long time because no backup route is available. To address this problem, configure BGP Best-external on the backup PE.
The following figure shows the networking with master and backup PEs.
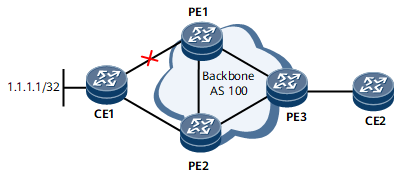
BGP Best-external must be enabled on the backup PE (PE2).
Configuration Procedures
Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
Run bgp as-number
The BGP view is displayed.
-
The device is enabled to select BGP Best-external routes.
Run peer { ipv4-address | group-name } advertise best-external
The device is enabled to advertise Best-external routes to the specified peer or peer group.
Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Verifying the Configuration
After configuring BGP Best-external, verify the configuration.
- Run the display bgp peer verbose command to check whether the device has been enabled to advertise BGP Best-external routes to a specified peer or peer group.