BGP Overview
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) advertises and maintains a large number of routes between autonomous systems (ASs).
Definition
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a dynamic routing protocol used between Autonomous Systems (ASs). BGP is widely used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
As three earlier-released versions of BGP, BGP-1, BGP-2, and BGP-3 are used to exchange reachable inter-AS routes, establish inter-AS paths, avoid routing loops, and apply routing policies between ASs.
Currently, BGP-4 is used.
BGP has the following characteristics:
Unlike an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP), such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Routing Information Protocol (RIP), BGP is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) which controls route advertisement and selects optimal routes between ASs rather than discovering or calculating routes.
BGP uses Transport Control Protocol (TCP) as the transport layer protocol, which enhances BGP reliability.
When routes are updated, BGP transmits only the updated routes, which reduces bandwidth consumption during BGP route distribution. Therefore, BGP is applicable to the Internet where a large number of routes are transmitted.
BGP provides many routing policies to flexibly select and filter routes.
BGP provides a mechanism that prevents route flapping, which effectively enhances Internet stability.
Purpose
BGP transmits route information between ASs. It, however, is not required in all scenarios.
BGP is required in the following scenarios:
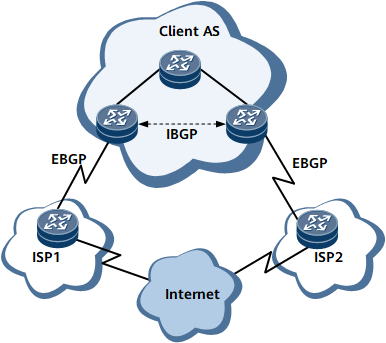
On the network shown in Figure 1, users need to be connected to two or more ISPs. The ISPs need to provide all or part of the Internet routes for the users. Routers, therefore, need to select the optimal route through the AS of an ISP to the destination based on the attributes carried in BGP routes.
The AS_Path attribute needs to be transmitted between users in different organizations.
Users need to transmit VPN routes through a Layer 3 VPN. For details, see the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series Feature Description - VPN.
Users need to transmit multicast routes and construct a multicast topology. For details, see the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series Feature Description - IP Multicast.
BGP is not required in the following scenarios: