Configuring the Next_Hop Attribute
Configuring the Next_Hop attribute allows for flexible control of BGP route selection.
Procedure
- Configure a device to change the next hop address of a route when the device advertises the route to an IBGP peer.
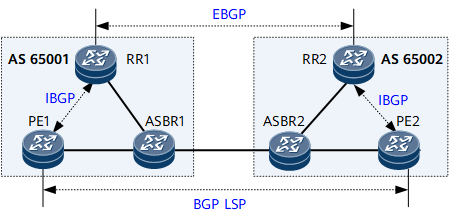
By default, a device does not change the next hop address of a route learned from an EBGP peer before forwarding the route to IBGP peers. The next hop address of a route advertised by an EBGP peer to this device is the peer address of the EBGP peer. After being forwarded to IBGP peers in the local AS, this route is not active because the next hop is unreachable. To address this problem, the relevant ASBR needs to be configured to change the Next_Hop of the route learned from an EBGP peer to the ASBR's own address before the ASBR advertises the route to an IBGP peer. As an IGP runs within the AS, the next hop of the route is reachable to the IBGP peer. As such, the route received by the IBGP peer is active.
- Prevent a device from changing the next hop address of a route imported from an IGP when the device advertises the route to an IBGP peer.
- Prevent an ASBR from changing the next hop address of a route when the ASBR advertises the route to an EBGP peer.
- Configure route-policy-based next hop recursion.
- Prevent the device from changing the next hop address of a route to ensure that traffic is transmitted along the optimal route when the device advertises the route to a peer in the following scenarios:
- The route is learned from a directly connected peer and is to be advertised to a directly connected EBGP peer, the original next hop of the route resides on the same network segment as the local interface that is used to establish the BGP peer relationship with the EBGP peer, and all directly connected interfaces are broadcast interfaces.
- The route is locally imported and is to be advertised to a directly connected IBGP or EBGP peer, the next hop to which the route recurses resides on the same network segment as the local interface that is used to establish the BGP peer relationship with the IBGP or EBGP peer, and all directly connected interfaces are broadcast interfaces.
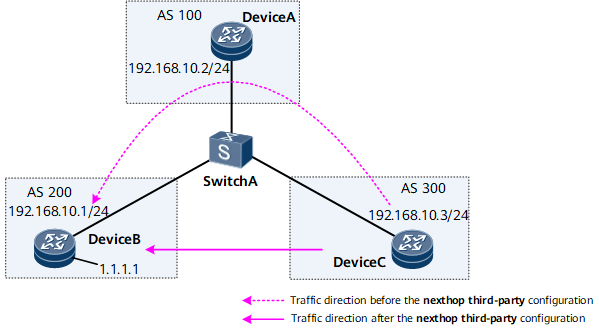
On the network shown in Figure 2, DeviceA establishes EBGP peer relationships with DeviceB and DeviceC, but DeviceB and DeviceC do not establish a peer relationship with each other.Assume that DeviceA receives an EBGP route 1.1.1.1 from DeviceB. If the nexthop third-party command is not run, the next hop address of the route is changed as follows:- Before DeviceB advertises the route 1.1.1.1 to DeviceA, DeviceB changes the next hop to 192.168.10.1.
- Before DeviceA advertises the route 1.1.1.1 to DeviceC, DeviceA changes the next hop to 192.168.10.2.
When traffic is transmitted from DeviceC to DeviceB, the traffic passes through DeviceA.
After the nexthop third-party command is run on DeviceA, the next hop address of the route 1.1.1.1 is changed as follows:- Before DeviceB advertises the route 1.1.1.1 to DeviceA, DeviceB changes the route next hop to 192.168.10.1.
- Before DeviceA advertises the route to DeviceC, DeviceA detects that the address (192.168.10.2) of its local interface that is used to establish the BGP peer relationship with DeviceC belongs to the same network segment as the original next hop address 192.168.10.1 of the route. Therefore, DeviceA does not change the next hop address of the route. As a result, the next hop address of the BGP route 1.1.1.1 received by DeviceC remains 192.168.10.1.
In this way, traffic from DeviceC can be directly forwarded to DeviceB, without passing through DeviceA.