Example for Configuring Dynamic BGP Peer Groups
Configuring dynamic BGP peer groups reduces network maintenance workload.
Networking Requirements
On a BGP network, multiple peers may frequently change, causing the establishment of peer relationships to change accordingly. If you configure peers in static mode, you need to frequently add or delete peer configurations on the local device, which increases the maintenance workload. To address this problem, configure the dynamic BGP peer function to enable BGP to listen for BGP connection requests from a specified network segment, dynamically establish BGP peer relationships, and add these peers to the same dynamic peer group. This spares you from adding or deleting BGP peer configurations in response to each change in BGP peers.
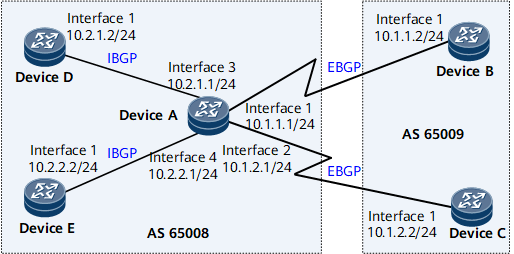
On the network shown in Figure 1, DeviceA, DeviceD, and DeviceE are in AS 65008, and DeviceB and DeviceC are in AS 65009. Because many devices are on the same network segment in an AS, you can configure dynamic peer groups on DeviceA.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure a dynamic IBGP peer group on DeviceA to listen for BGP connection requests from network segment 10.2.0.0/16.
Configure a dynamic EBGP peer group on DeviceA to listen for BGP connection requests from network segment 10.1.0.0/16.
Configure IBGP connections between DeviceD and DeviceA, and between DeviceE and DeviceA.
Configure EBGP connections between DeviceB and DeviceA, and between DeviceC and DeviceA.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
AS numbers of DeviceA, DeviceD, and DeviceE
AS numbers of DeviceB and DeviceC
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure dynamic BGP peer groups.
# Configure dynamic BGP peer groups on DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] bgp 65008 [*DeviceA-bgp] bgp dynamic-session-limit 5 [*DeviceA-bgp] group a listen internal [*DeviceA-bgp] peer a listen-net 10.2.0.0 16 [*DeviceA-bgp] group b listen external [*DeviceA-bgp] peer b listen-as 65009 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer b listen-net 10.1.0.0 16 [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
- Configure IBGP connections.
# Configure DeviceD.
[~DeviceD] bgp 65008 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceD-bgp] commit [~DeviceD-bgp] quit
# Configure DeviceE.
[~DeviceE] bgp 65008 [*DeviceE-bgp] peer 10.2.2.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceE-bgp] commit [~DeviceE-bgp] quit
- Configure EBGP connections.
# Configure DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65009 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure DeviceC.
[~DeviceC] bgp 65009 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.1.2.1 as-number 65008 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Check the status of BGP connections.
[~DeviceA] display bgp peer Status codes: * - Dynamic BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.1 Local AS number : 65008 Total number of peers : 4 Peers in established state : 4 Total number of dynamic peers : 4 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv *10.1.1.2 4 65009 8 7 0 00:04:16 Established 0 *10.1.2.2 4 65009 5 5 0 00:02:01 Established 0 *10.2.1.2 4 65008 5 5 0 00:02:01 Established 0 *10.2.2.2 4 65008 5 5 0 00:02:01 Established 0
The command output shows that DeviceA has established BGP connections with other routers and the connection status is Established.
# Check information about BGP peer groups.
[~DeviceA] display bgp group a BGP peer-group : a Remote AS : 65008 Authentication type configured : None Type : listen internal Configured hold timer value : 180 Keepalive timer value : 60 Connect-retry timer value : 32 Minimum route advertisement interval is 15 seconds PeerSession Members : 10.2.1.2 10.2.2.2 Peer Preferred Value: 0 No routing policy is configured Peer Members: Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv *10.2.1.2 4 65008 3 4 0 00:00:20 Established 0 *10.2.2.2 4 65008 3 4 0 00:00:21 Established 0 [~DeviceA] display bgp group b BGP peer-group : b Remote AS : 65009 Authentication type configured : None Type : listen external Configured hold timer value : 180 Keepalive timer value : 60 Connect-retry timer value : 32 Minimum route advertisement interval is 15 seconds PeerSession Members : 10.1.1.2 10.1.2.2 Peer Preferred Value: 0 No routing policy is configured Peer Members: Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv *10.1.1.2 4 65009 3 4 0 00:00:20 Established 0 *10.1.2.2 4 65009 3 4 0 00:00:21 Established 0
The command output shows that two dynamic peer groups a and b exist on DeviceA and each dynamic peer group has two peers, indicating that the dynamic peer groups are properly established.
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 bgp dynamic-session-limit 5 group a listen internal peer a listen-net 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 group b listen external peer b listen-as 65009 peer b listen-net 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 # ipv4-family unicast peer a enable peer b enable # return
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65009 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.1.1 enable # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65009 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.1.2 enable # return
DeviceD configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.2.1.1 enable # return
DeviceE configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65008 peer 10.2.2.1 as-number 65008 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.2.2.1 enable # return