Configuring the POPGO Function
After the POPGO function is configured on the egress of a BGP LSP, the egress forwards each data packet received from the LSP through the outbound interface found in the ILM based on the label information carried in the packet.
Usage Scenario
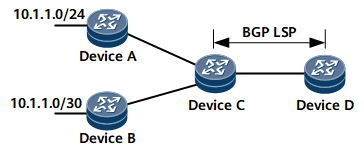
On the network shown in Figure 1, DeviceC has two static routes, 10.1.1.0/24 and 10.1.1.0/30, and the next hops of the two routes are DeviceA and DeviceB respectively. DeviceC only imports route 10.1.1.0/24 to BGP and then sends this route to DeviceD. A BGP LSP is established between DeviceC and DeviceD. By default, after DeviceC receives a data packet addressed to 10.1.1.0 from DeviceD, DeviceC removes the LSP label from the packet, searches for an outbound interface in the IP forwarding table according to the longest-match principle, and incorrectly sends the packet to DeviceB.
To solve the preceding problem, configure the apply-label per-route pop-go command on DeviceC. After the apply-label per-route pop-go command is configured, when DeviceC sends route 10.1.1.0/24 to DeviceD, DeviceC records in the ILM the mapping between the label assigned to the route and the outbound interface of the route. Then, after the DeviceC receives a data packet from DeviceD, DeviceC directly searches the ILM for an outbound interface based on label information carried in the packet and forwards the packet through the found outbound interface after removing the packet label. This implementation ensures correct packet forwarding.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bgp as-number
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run apply-label per-route pop-go
The POPGO function is configured.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Checking the Configurations
After configuring the POPGO function, you can run the following command to check the configuration.
Run the display mpls lsp protocol bgp command. The command output shows detailed BGP LSP information. If POPGO is displayed in the Label Operation field, the POPGO function is successfully configured.