Configuring the BGP Next Hop Recursion Change Delayed Response
Configuring the BGP next hop recursion change delayed response can minimize traffic loss during route changes.
Usage Scenario
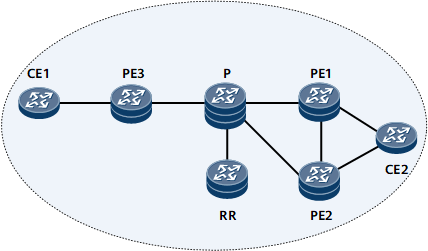
As shown in Figure 1, PE1, PE2, and PE3 are the clients of the RR. CE2 is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2. PE1 and PE2 advertise their routes to CE2 to the RR. The RR advertises the route from PE1 to PE3. PE3 has a route to CE2 only and advertises this route to CE1. After the route exchange, CE1 and CE2 can communicate. If PE1 fails, PE3 detects that the next hop is unreachable and instructs CE1 to delete the route to CE2. Traffic is interrupted. After BGP route convergence is complete, the RR selects the route advertised by PE2 and sends a route update message to PE3. PE3 then advertises this route to CE1, and traffic forwarding is restored to the normal state. A high volume of traffic will be lost during traffic interruption because BGP route convergence is rather slow.
If the BGP next hop recursion change delayed response is enabled on PE3, PE3 does not reselect a route or instruct CE1 to delete the route to CE2 immediately after detecting that the route to PE1 is unreachable. After BGP convergence is complete, the RR selects the route advertised by PE2 and sends the route to PE3. PE3 then reselects a route and sends a route update message to CE1. Traffic forwarding is restored to the normal state. After the BGP next hop recursion changes delayed response is enabled on PE3, PE3 does not need to delete the route or instruct CE1 to delete the route. This delayed response speeds up BGP route convergence and minimizes traffic loss.

The BGP next hop delayed response applies to a scenario where the next hop has multiple links to reach the same destination. If there is only one link between the next hop and the destination, configuring the BGP next hop delayed response may cause heavier traffic loss when the link fails because link switching is impossible.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring the BGP next hop recursion change delayed response, complete the following task:
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bgp { as-number-plain | as-number-dot }
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run nexthop recursive-lookup delay [ delay-time ]
A delay in responding to a next hop recursion change is set.
After the nexthop recursive-lookup delay command is run, the device delays responses to all recursion changes. After the nexthop recursive-lookup non-critical-event delay command is run, the device delays responses only to non-critical BGP recursion changes. If both commands are run, the nexthop recursive-lookup non-critical-event delay command takes precedence over the nexthop recursive-lookup delay command.
The delay time specified in the nexthop recursive-lookup non-critical-event delay command must be greater than or equal to that specified in the nexthop recursive-lookup delay command if both commands are run.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Checking the Configurations
After configuring the BGP next hop recursion changes delayed response, you can run the following command to check the previous configuration.
- Run the display current-configuration configuration bgp | include nexthop recursive-lookup delay command to view information about the delay in responding to a next hop recursion change.
- Run the display current-configuration configuration bgp | include nexthop recursive-lookup non-critical-event delay command to view information about the delay in responding to non-urgent next hop recursion changes.