Origin
The Origin attribute indicates how routes become BGP routes.
- IGP: indicates that routes are added to the BGP routing table using the network command. IGP has the highest priority.
- EGP: indicates that routes are learned through the EGP protocol. EGP has the second highest priority.

The NetEngine 8000 F can receive and send BGP routes with EGP as the Origin. However, the NetEngine 8000 F does not support the EGP protocol; therefore, to set the Origin of routes to EGP, you need to run the apply origin { egp { as-number-plain | as-number-dot } | igp | incomplete } command to configure an apply clause for a route-policy.
- Incomplete: indicates that routes are added to the BGP routing table using the import-route command. Incomplete has the lowest priority.
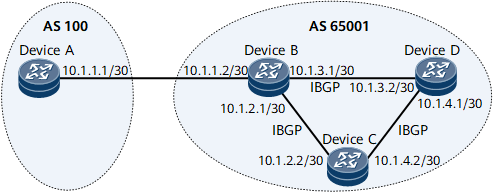
The configurations on Device D are as follows:
# bgp 65001 # ipv4-family unicast network 10.1.4.0 255.255.255.252 //Advertise the route 10.1.4.0/30. #
The configurations on Device C are as follows:
# bgp 65001 # ipv4-family unicast import-route direct //Import direct routes. #
Run the display bgp routing-table [ ip-address ] command to check the configurations.
# Display the routing table of Device B.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 3 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn i 10.1.2.0/30 10.1.2.2 0 100 0 ? *>i 10.1.4.0/30 10.1.3.2 0 100 0 i * i 10.1.2.2 0 100 0 ?
The preceding command output shows that two active routes 10.1.4.0/30 are available in the routing table.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table 10.1.4.0 BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.2 Local AS number : 65001 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select BGP routing table entry information of 10.1.4.0/30: From: 10.1.3.2 (10.1.3.2) Route Duration: 01h14m48s Relay IP Nexthop: 0.0.0.0 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Original nexthop: 10.1.3.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path Nil, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, active, pre 255 Advertised to such 1 peers: 10.1.1.1 BGP routing table entry information of 10.1.4.0/30: From: 10.1.2.2 (10.1.2.2) Route Duration: 01h13m20s Relay IP Nexthop: 0.0.0.0 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Original nexthop: 10.1.2.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, pre 255, not preferred for Origin Not advertised to any peer yet
The preceding command output shows that the route learned from Device D is selected because it is imported using the network command and its Origin priority is higher than that of the route learned from Device C. Table 1 describes the attribute comparison of the routes learned from Device C and Device D.
Route Attribute |
Route Learned from Device C |
Route Learned from Device D |
Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
PrefVal |
0 |
0 |
The same. |
Local_Pref |
100 |
100 |
The same. |
Route type |
Learned from a peer |
Learned from a peer |
The same. |
AIGP |
- |
- |
The same. |
AS_Path |
- |
- |
The same length. |
Origin |
Incomplete |
IGP |
The route learned from Device D is optimal. |
The Origin attribute can be modified using a route-policy. In the following example, a route-policy is configured on Device B to modify the Origin attribute, and the detailed configurations are as follows:
# bgp 65001 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.3.2 route-policy for_d import //Apply import policy named for_d to the routes learned from 10.1.3.2 and use for_d to modify the Origin value. # route-policy for_d permit node 10 //Define the route-policy named for_d. apply origin incomplete //Set the Origin type to Incomplete.
Run the display bgp routing-table [ ip-address ] command to check the configurations.
# Display the routing table of Device B.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 3 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn i 10.1.2.0/30 10.1.2.2 0 100 0 ? *>i 10.1.4.0/30 10.1.2.2 0 100 0 ? * i 10.1.3.2 0 100 0 ?
The preceding command output shows that the route learned from Device C becomes the optimal route.
[~DeviceB] display bgp routing-table 10.1.4.0 BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.2 Local AS number : 65001 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select BGP routing table entry information of 10.1.4.0/30: From: 10.1.2.2 (10.1.2.2) Route Duration: 01h28m19s Relay IP Nexthop: 0.0.0.0 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Original nexthop: 10.1.2.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, active, pre 255 Advertised to such 1 peers: 10.1.1.1 BGP routing table entry information of 10.1.4.0/30: From: 10.1.3.2 (10.1.3.2) Route Duration: 00h03m18s Relay IP Nexthop: 0.0.0.0 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Original nexthop: 10.1.3.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path Nil, origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, pre 255, not preferred for router ID Not advertised to any peer yet
The preceding command output shows that the route learned from Device C becomes the optimal route because it has a smaller router ID than the route learned from Device D. Table 2 describes the attribute comparison of the routes learned from Device C and Device D.
Route Attribute |
Route Learned from Device C |
Route Learned from Device D |
Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
PrefVal |
0 |
0 |
The same. |
Local_Pref |
100 |
100 |
The same. |
Route type |
Learned from a peer |
Learned from a peer |
The same. |
AIGP |
- |
- |
The same. |
AS_Path |
- |
- |
The same. |
Origin |
Incomplete |
Incomplete |
The same. |
MED |
0 |
0 |
The same. |
Peer type |
IBGP |
IBGP |
The same. |
IGP cost |
- |
- |
The same. |
Cluster_List |
- |
- |
The same. |
Router ID |
10.1.2.2 |
10.1.3.2 |
The route learned from Device C is optimal. |