Overview of BPDU Tunneling
A bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) tunnel is a path along which BPDUs are transparently transmitted over a carrier network.
Definition
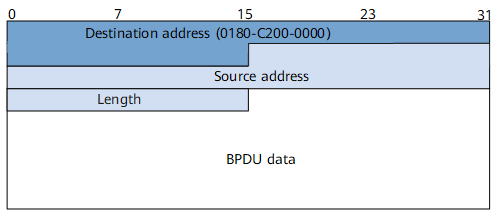
BPDUs are Layer 2 protocol packets. As shown in Figure 1, BPDUs are encapsulated using IEEE 802.3 and are transmitted in multicast mode.
BPDUs are used to transmit Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) information. The path along which BPDUs are transparently transmitted over a carrier network is known as a Layer 2 protocol tunnel or a BPDU tunnel.
Table 1 lists fields in a BPDU.
Background
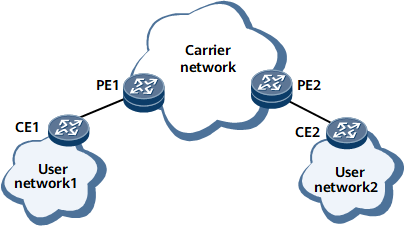
As shown in Figure 2, MSTP runs on user networks 1 and 2. BPDUs from user networks 1 and 2 need to be transparently transmitted over the carrier network and need to reach each other to perform the spanning tree calculation. When BPDUs from user network 1 reach PE1 on the carrier network, PE1 cannot determine whether these BPDUs are transmitted from a user network or a carrier network, because all BPDUs contain the same destination MAC address 0180-C200-0000. PE1 then sends all the BPDUs to its central processing unit (CPU) for processing and performs the spanning tree calculation.
In this situation, devices on user network 1 perform the spanning tree calculation with PE1, instead of devices on user network 2. As a result, BPDUs from user network 1 cannot reach user network 2.
To address this problem, BPDUs must be transparently transmitted over the carrier network. To implement the transparent transmission, the following conditions must be met:
Branches of a user network can exchange BPDUs.
BPDUs sent from a user network cannot be processed by the CPUs on carrier network devices.
BPDUs from different user networks must be isolated and free from interference.
Configuring BPDU tunneling on carrier network devices meets the preceding conditions. After BPDU tunneling is configured, the carrier network can transparently transmit BPDUs between user networks through BPDU tunnels.