Example for Configuring Y.1731 ETH-LCK EVPN
This section uses typical E2E networking as an example to describe how to use the ETH-LCK function EVPN networking.
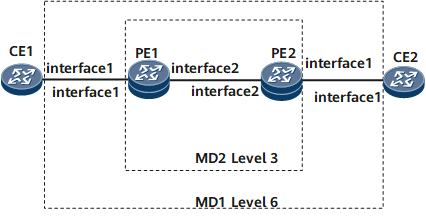
Networking Requirements
AIS is used to prevent a MEP in an MD of a higher level from sending the same trap as that sent by a MEP in an MD of a lower level to the NMS. As shown in Figure 1, PE1 and PE2 are connected through an EVPN, and CE1 and CE2 are connected to the EVPN through a BD. Configure the ETH-LCK function for the BD on the PE. A MEP in the inner MD with a lower level initiates ETH-Test by sending an ETH-LCK frame to a MEP in the outer MD. Upon receipt of the ETH-LCK frame, the MEP in the outer MD suppresses all CC alarms immediately and reports an ETH-LCK alarm indicating administrative locking. In this way, alarm suppression is implemented.
Configuration Roadmap
- Configure the EVPN network between PE1 and PE2.
Add the PEs to an MD, add each PE and its attached CE to an MD, and ensure that the level of the MD to which the PEs belong is lower than that to which each PE and its attached CE belong.
Configure ETH-LCK to suppress MEPs in MDs of different levels from sending the same trap to the NMS.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
EVPN instance name evpna, RD value, and RT value
MD name, MA name, and MEP IDs for configuring basic CFM functions
Procedure
- Configure the AC-side link ETH-LCK.
Configure an EVPN connection.
Configure an EVPN connection between PE1 and PE2. The configuration details are not provided here. For details, see the EVPN Configuration or configuration files in this configuration example.
Configure basic Ethernet CFM functions, set the MEP type to Inward, and enable the ETH-LCK function.
Configure basic Ethernet CFM functions on each PE. Specify the Ethernet CFM protocol as IEEE Standard 802.1ag-2007. Create an MD named md1 and an MA named ma1, and bind the MA to the EVPN instance.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] cfm enable [*PE1] cfm md md1 level 3 [*PE1-md-md1] ma ma1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] map evpn vpn-instance evpna [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 1 interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 inward [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 1 lck enable level 6 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep mep-id 2 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] eth-test enable mep 1 [*PE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] commit
The configuration on PE2 is similar to that on PE1. For details, see the configuration file.
- Configure basic Ethernet CFM functions on CE1.
Specify the Ethernet CFM protocol as IEEE Standard 802.1ag-2007. Create an MD named md1 and an MA named ma1, and bind the MA to the EVPN instance.
[~CE1] cfm enable [*CE1] cfm md md1 leve 6 [*CE1-md-md1] ma ma1 [*CE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] map vlan 10 [*CE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep mep-id 1 interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 outward [*CE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable [*CE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep mep-id 2 [*CE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable [*CE1-md-md1-ma-ma1] commit
The configuration of CE2 is similar to that of CE1. For details, see the configuration file.
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # cfm enable # evpn vpn-instance evpna route-distinguisher 100:1 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown evpn binding vpn-instance evpna # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # l2vpn-family evpn peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # evpn source-address 1.1.1.1 # cfm md md1 level 3 ma ma1 map evpn vpn-instance evpna mep mep-id 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 inward mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable mep mep-id 1 lck enable level 6 remote-mep mep-id 2 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable eth-test enable mep 1 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # cfm enable # evpn vpn-instance evpna route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown evpn binding vpn-instance evpna # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # l2vpn-family evpn peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # evpn source-address 2.2.2.2 # cfm md md1 level 3 ma ma1 map evpn vpn-instance evpna mep mep-id 2 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 inward mep ccm-send mep-id 2 enable mep mep-id 1 lck enable level 6 remote-mep mep-id 1 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 1 enable eth-test enable mep 2 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 10 # cfm enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswtich undo shutdown port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # cfm md md1 level 6 ma ma1 map vlan 10 mep mep-id 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 outward mep ccm-send mep-id 1 enable remote-mep mep-id 2 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 2 enable # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # vlan batch 10 # cfm enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # cfm md md1 level 6 ma ma1 map vlan 10 mep mep-id 2 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 outward mep ccm-send mep-id 2 enable remote-mep mep-id 1 remote-mep ccm-receive mep-id 1 enable # return