Configuring Dual-Root 1+1 Protection
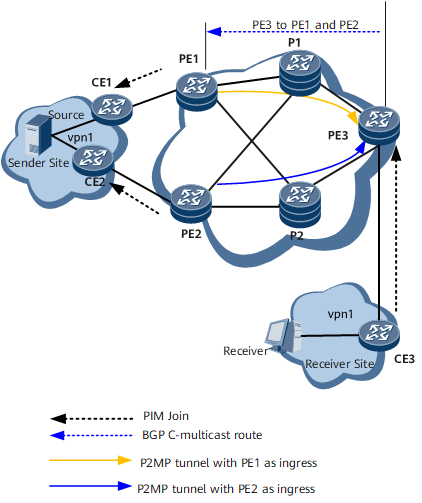
Configuring dual-root 1+1 protection accelerates multicast service convergence and improves reliability in case a sender PE on a P2MP tunnel fails.
Usage Scenario
Pre-configuration Tasks
RSVP-TE P2MP Tunnel:
Configure NG MVPN.
Configure BFD for P2MP TE on the root nodes.
Configure VPN FRR on the leaf nodes.
Globally enable BFD on the root and leaf nodes.
mLDP P2MP Tunnel:
Configure NG MVPN.
Configure BFD for mLDP P2MP on the root and leaf nodes.
Configure VPN FRR on the leaf nodes.
Globally enable BFD on the root and leaf nodes.

If static default routes are configured on leaf nodes, to enable the leaf nodes to forward received BFD detection packets properly, configure IPv4 route import between VPN and public network instances so that public network routes can be replicated to the NG MVPN instance. For details on how to import public network routes into an NG MVPN instance, see Configuring Route Import Between VPN and Public Network Instances. Ensure that the specified route-policy has been configured using the route-policy command.
Configure NG MVPN.
Configure VPN FRR on the leaf nodes.
Perform the following steps on the leaf nodes:
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ip vpn-instancevpn-instance-name
The VPN instance view is displayed.
- Run ipv4-family
The VPN instance IPv4 address family view is displayed.
- Run mvpn
The VPN instance IPv4 address family MVPN view is displayed.
- Run c-multicast frr
C-multicast FRR is enabled. C-multicast FRR allows VPN multicast traffic to be imported to the primary and backup tunnels.
- (Only for multicast traffic detection based C-multicast FRR) Run c-multicast frr flow-detection-based
Multicast traffic detection based C-multicast FRR is enabled.
- (Optional) Run multicast wtrwtr-time
A switchback wait time is set for C-multicast FRR in NG MVPN 1+1 scenarios.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Verifying the Configuration
After configuring dual-root 1+1 protection, check the configurations.
Run the display pim [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | all-instance ] routing-table [ group-address [ mask { group-mask-length | group-mask } ] | source-address [ mask { source-mask-length | source-mask } ] | incoming-interface { interface-type interface-number | register | through-bgp } | outgoing-interface { include | exclude | match } { interface-type interface-number | register | none | pseudo } | mode { ssm | sm } | flags flag-value | fsm ] * [ outgoing-interface-number [ number ] ] command to check information about the PIM routing table.
# Run the display pim [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | all-instance ] routing-table command. The command output shows backup PIM entries in the PIM routing table.