Example for Enabling the Highest IP Address to Be Selected as the UMH on an NG MVPN
This section provides an example for enabling the highest IP address to be selected as the UMH on an NG MVPN.
Networking Requirements
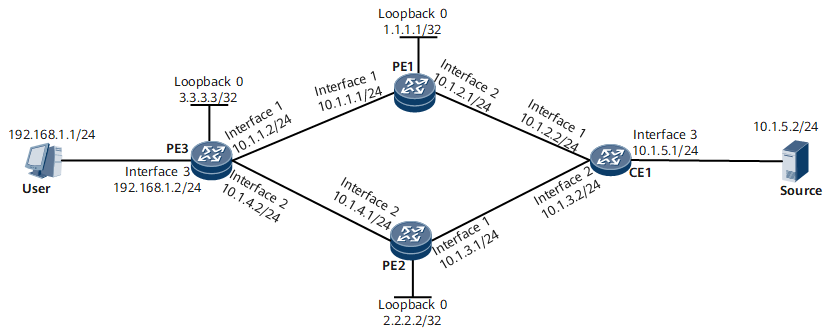
On an NG MVPN, when multiple sender PEs exist, receiver PEs select routes based on preferred unicast routes by default. On the network shown in Figure 1, the receiver PE is PE3, and the sender PEs are PE1 and PE2. By default, the path to the source that PE3 selects based on preferential unicast routes is PE3-PE1-CE1. If the system is enabled to select the highest IP address as the UMH on PE3, the path selected is PE3-PE2-CE1.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure BGP/MPLS IP VPN and ensure that unicast VPN services are properly transmitted. (In this example, ensure that the source and user can communicate.)
Enable mLDP on all PEs globally and ensure that the PEs can use mLDP to establish P2MP tunnels.
Enable all PEs to establish BGP MVPN peer relationships and configure BGP to transmit A-D and C-multicast routes.
Configure PE1 and PE2 to use mLDP to establish an I-PMSI tunnel so that an mLDP P2MP LSP can be triggered.
Configure PIM on PE1 and PE2 interfaces bound to VPN instances and on CE1 interfaces connecting to PEs to allow a VPN multicast routing table to be established to guide multicast traffic forwarding.
Enable the highest IP address to be selected as the UMH in the VPN instance IPv4 address family MVPN view of PE3.
Configure IGMP on the interfaces connecting a multicast device to a user network segment to allow the device to manage multicast group members on the network segment.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Public network OSPF process ID: 1; area ID: 0
VPN instance name on PE1, PE2, and PE3: VPNA (other data is shown in Figure 1)
Procedure
- Configure BGP/MPLS IP VPN.
- Enable mLDP globally.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] commit [~PE1-mpls-ldp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls ldp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] commit [~PE2-mpls-ldp] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] mpls ldp [*PE3-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE3-mpls-ldp] commit [~PE3-mpls-ldp] quit
- Establish a BGP MVPN peer relationship between the PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] commit [~PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [~PE2-bgp] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bgp 100 [*PE3-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE3-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE3-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*PE3-bgp-af-mvpn] commit [~PE3-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [~PE3-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp mvpn all peer command on the PEs. The command output shows that PE1 has established a BGP MVPN peer relationship with PE2 and PE3. The following example uses the command output on PE3.
[~PE3] display bgp mvpn all peer BGP local router ID : 3.3.3.3 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 1.1.1.1 4 100 87 89 0 01:10:28 Established 0 2.2.2.2 4 100 87 88 0 01:09:36 Established 0 - Configure each PE to use mLDP to establish an I-PMSI tunnel.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] ip vpn-instance VPNA [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] sender-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] rpt-spt mode [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] ipmsi-tunnel [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] mldp [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-VPNA] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] multicast mvpn 2.2.2.2 [*PE2] ip vpn-instance VPNA [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] sender-enable [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] rpt-spt mode [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] ipmsi-tunnel [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] mldp [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-VPNA] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] multicast mvpn 3.3.3.3 [*PE3] ip vpn-instance VPNA [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA] ipv4-family [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] rpt-spt mode [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA] quit [*PE3] commit
After the configurations are complete, run the display mvpn vpn-instance ipmsi command on the PEs to check I-PMSI tunnel information. The following example uses the command output on PE3.
[~PE3] display mvpn vpn-instance VPNA ipmsi MVPN local I-PMSI information for VPN-Instance: VPNA Tunnel type: mLDP P2MP LSP Tunnel state: -- Root-ip: 1.1.1.1 Opaque value: 0x01000400008001 Root: 1.1.1.1 Leaf: 1: 3.3.3.3 (local) Tunnel type: mLDP P2MP LSP Tunnel state: -- Root-ip: 2.2.2.2 Opaque value: 0x01000400008001 Root: 2.2.2.2 Leaf: 1: 3.3.3.3 (local)The command outputs show that two mLDP P2MP LSPs have been established, with PE1 and PE2 as the root nodes respectively and PE3 as the leaf node.
- Configure PIM.
# Configure PE1.
[*PE1] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[*PE2] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure PE3.
[*PE3] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE3] commit
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] multicast routing-enable [*CE1] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*CE1] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE1] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE1] commit
- Enable the highest IP address to be selected as the UMH in the VPN instance IPv4 address family MVPN view of PE3.
[*PE3] ip vpn-instance VPNA [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA] ipv4-family [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] umh-select highest-ip [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA-af-ipv4] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-VPNA] quit
- Configure IGMP and IGMP version 3.
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] igmp enable [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] igmp version 3 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After the preceding configurations are complete, run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance VPNA command on PE3. The command output shows that the next hop of the optimal unicast path is PE1.
[~PE3] display ip routing-table vpn-instance VPNA Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : VPNA Destinations : 8 Routes : 8 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.2.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 1.1.1.1 0/1/0 10.1.3.0/24 IBGP 255 2 RD 2.2.2.2 0/1/1 10.1.5.0/24 IBGP 255 3 RD 1.1.1.1 0/1/0 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 192.168.1.2 0/1/2 192.168.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 0/1/2 192.168.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 0/1/2 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display pim vpn-instance VPNA routing-table command on PE3. The command output shows that the UMH of the route selected based on the highest IP address is PE2. When the source sends multicast traffic to the source group, the user can receive the multicast traffic and the traffic travels along the path PE3-PE2-CE1.
[~PE3] display pim vpn-instance VPNA routing-table VPN-Instance: VPNA Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.5.2, 224.1.1.1) RP: NULL Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT SG_RCVR UpTime: 00:22:17 Upstream interface: through-BGP, Refresh time: 00:22:17 Upstream neighbor: 2.2.2.2 RPF prime neighbor: 2.2.2.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: 0/1/2 Protocol: static, UpTime: 00:22:17, Expires: -
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.5.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # return
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 # ip vpn-instance VPNA ipv4-family route-distinguisher 300:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 3:3 export-extcommunity vpn-target 3:3 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp rpt-spt mode ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mldp-p2mp-tunnel p2mp-lsp # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance VPNA ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance VPNA import-route direct import-route static # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # returnPE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # multicast mvpn 2.2.2.2 # ip vpn-instance VPNA ipv4-family route-distinguisher 300:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 4:4 export-extcommunity vpn-target 4:4 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp rpt-spt mode ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mldp-p2mp-tunnel p2mp-lsp # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance VPNA ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance VPNA import-route direct import-route static # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.4.0 0.0.0.255 # returnPE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # multicast mvpn 3.3.3.3 # ip vpn-instance VPNA ipv4-family route-distinguisher 400:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 3:3 export-extcommunity vpn-target 4:4 export-extcommunity vpn-target 3:3 import-extcommunity vpn-target 4:4 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn c-multicast signaling bgp rpt-spt mode umh-select highest-ip # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance VPNA ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp static-group 224.1.1.1 source 10.1.5.2 # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance VPNA network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.4.0 0.0.0.255 # return