Example for Configuring Intra-AS Segmented Tunnel Transport (Through mLDP P2MP Tunnel Stitching)
This section provides an example for configuring intra-AS segmented tunnel transport (through mLDP P2MP tunnel stitching).
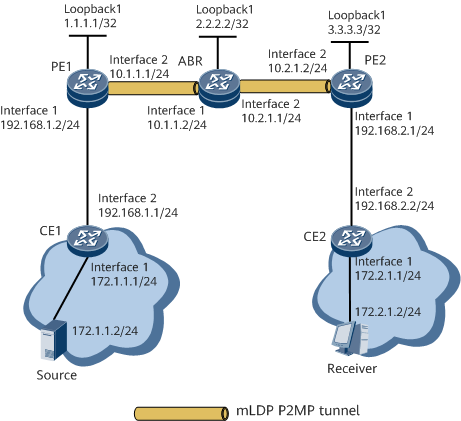
Networking Requirements
NG MVPN is deployed on the service provider's backbone network to solve multicast service issues that arise due to traffic congestion, transmission reliability, and data security. On the backbone network shown in Figure 1, LDP LSPs are deployed in different areas to carry BGP/MPLS IP VPN services. The customer requires that MVPN services be provided using the existing network. To meet the preceding requirements, deploy segmented NG MVPN over an mLDP P2MP stitching tunnel.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure BGP/MPLS IP VPN and ensure that unicast VPN services are properly transmitted.
Establish a BGP MVPN peer relationship between the PEs so that the PEs can use BGP to exchange A-D and C-multicast routes.
- Configure NG MVPN to support intra-AS inter-area segmented tunnels.
Configure PE1 to use mLDP to establish an I-PMSI tunnel so that an mLDP P2MP tunnel from PE1 to the ABR is established.
- Configure the ABR to use mLDP to establish a stitching tunnel to PE2 so that an mLDP P2MP tunnel from the ABR to PE2 is established.
Bind the VPN instance to each PE's interface through which a CE accesses and configure PIM on the interfaces connecting PEs and CEs so that VPN multicast routing entries are generated for multicast traffic forwarding.
Configure IGMP on CE2's interface connected to the multicast receiver so that CE2 manages the receiver (multicast group member).
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
ID (2) of the IS-IS process running between PE1 and the ABR System ID (45.0005.0005.0006.00) of PE2, and system ID (45.0005.0005.0005.00) of the ABR
- OSPF process ID (10) on PE2 and the ABR
On PE1 and PE2: VPN instance name (vpn1), VPN target (100:100), RD (100:1) of PE1, and RD (200:1) of PE2
- AS number (100) for the BGP peers on the public network
- ID (2) of the OSPF process, through which CE1 interworks with PE1, and CE2 interworks with PE2
Procedure
- Configure BGP/MPLS IP VPN.
- Establish a BGP MVPN peer relationship between each PE and the ABR, and configure the ABR as the RR for PE1 and PE2.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure the ABR.
[~ABR] bgp 100 [*ABR-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] undo policy vpn-target [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [*ABR-bgp] quit [*ABR] commit
- Configure NG MVPN to support intra-AS inter-area segmented tunnels.
Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] multicast routing-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] inter-area-segmented enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] commit
Configure the ABR.
[~ABR] multicast mvpn inter-area-segmented enable [*ABR] commit
- Configure PE1 and the ABR to use mLDP to establish an I-PMSI tunnel in between, and configure the ABR and PE2 to use mLDP to establish a stitching PMSI tunnel in between.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE1] multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] sender-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] ipmsi-tunnel [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] mldp [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn-ipmsi] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure the ABR.
[~ABR] multicast mvpn 2.2.2.2 [*ABR] route-policy rp1 permit node 1 [*ABR-route-policy-rp1]apply stitch-pmsi mldp [*ABR-route-policy-rp1]quit [*ABR] bgp 100 [*ABR-bgp] ipv4-family mvpn [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] reflect change-path-attribute //Enable the RR to modify path attributes of BGP MVPN routes based on an export policy. [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] peer 6.6.6.6 route-policy rp1 export [*ABR-bgp-af-mvpn] quit [*ABR-bgp] quit [*ABR] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] multicast mvpn 3.3.3.3 [*PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] mvpn [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4-mvpn] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE2] commit
After the configuration is complete, run the display mvpn inter-region-segmented ipmsi command on the ABR to check I-PMSI tunnel information.
[~ABR] display mvpn inter-region-segmented ipmsi Inter-region-segmented I-PMSI routes: total 1 I-PMSI(RD:OrigIP): 100:100: 1.1.1.1 Received Upstream I-PMSI: Tunnel type: mLDP P2MP LSP, Root-IP: 1.1.1.1, Opaque value: 0x01000400008041 Leaf: 1: 2.2.2.2 (local) Advertised Downstream I-PMSI(Policy: rp1): Tunnel type: mLDP P2MP LSP, Root-IP: 2.2.2.2, Opaque value: 0x01000400008001 Leaf: 1: 3.3.3.3The command output shows that an mLDP P2MP tunnel has been established, with PE1 as the root and the ABR as a leaf. In addition, an mLDP P2MP stitching tunnel has been established, with the ABR as the root and PE2 as a leaf.
- Configure PIM.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] multicast routing-enable [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] multicast routing-enable [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/2 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE2] commit
- Configure IGMP.
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/1 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] igmp enable [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE2] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After the configuration is complete, segmented NG MVPN functions are configured. If CE2 has access users, CE1 can use the BGP/MPLS IP VPN to forward multicast data to the users. In this example, the user connected to CE2 sends an IGMP Report message to CE2, and the multicast source 172.16.1.2 sends multicast data. A check on multicast routing entries can determine whether the segmented NG MVPN is configured successfully.
Run the display pim routing-table command on CE2 to view its PIM routing table. Run the display pim vpn-instance vpn1 routing-table command on PE2 to check the PIM routing entries of vpn1.
[~CE2] display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (172.16.1.2, 239.1.1.1) RP: NULL Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT SG_RCVR ACT UpTime: 08:48:25 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2, Refresh time: 08:48:25 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.2.1 RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.2.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Protocol: igmp, UpTime: 08:48:25, Expires: - [~PE2] display pim vpn-instance vpn1 routing-table VPN-Instance: vpn1 Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (172.16.1.2, 239.1.1.1) RP: NULL Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT UpTime: 00:05:16 Upstream interface: through-BGP, Refresh time: 00:05:16 Upstream neighbor: 2.2.2.2 RPF prime neighbor: 2.2.2.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:05:16, Expires: 00:03:16
Configuration Files
CE1
# sysname CE1 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE1
# sysname PE1 # multicast mvpn 1.1.1.1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:100 vpn-target 100:100 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:100 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp inter-area-segmented enable ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # ipv4-family # isis 2 network-entity 45.0005.0005.0006.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 2 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 isis enable 2 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route ospf 2 # ospf 2 vpn-instance vpn1 import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # returnCE2
# sysname CE2 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE2
# sysname PE2 # multicast mvpn 3.3.3.3 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 100:100 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:100 import-extcommunity multicast routing-enable mvpn c-multicast signaling bgp # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # ipv4-family # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route ospf 2 # ospf 10 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf 2 vpn-instance vpn1 import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
ABR
# sysname ABR # multicast mvpn 2.2.2.2 # multicast mvpn inter-area-segmented enable # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # ipv4-family # isis 2 network-entity 45.0005.0005.0005.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 2 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 2 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local # ipv4-family mvpn reflect change-path-attribute undo policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 route-policy rp1 export peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local # ipv4-family vpnv4 undo policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 reflect-client peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 reflect-client peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local # ospf 10 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy rp1 permit node 1 apply stitch-pmsi mldp # return