Example for Configuring DHCP Snooping for a Layer 3 Device
This section provides an example for configuring Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping for a Layer 3 device.
Networking Requirements
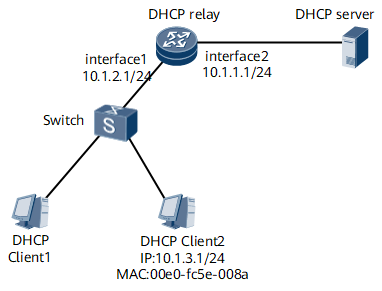
As shown in Figure 1, DHCP clients are connected to DHCP relay through the switch. Configure DHCP snooping on the Layer 3 interfaces, GE0/1/0 and GE0/1/1, of the DHCP relay. Configure the interfaces connecting to DHCP clients as untrusted interfaces and the interface connecting to the DHCP relay as a trusted interface.
If a user abnormally logs out after obtaining an IP address, the system automatically detects this fault, deletes the entry in the DHCP binding table, and instructs the DHCP server to release the IP address.
Configure DHCP snooping on the DHCP relay to prevent the following attacks:
Bogus DHCP server attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks and IP/MAC address spoofing
Denial of service (DoS) attacks by changing the CHADDR field value
Attacks by sending bogus DHCP request packets for extending IP lease
Attacks by sending the DHCP request packets
DHCP client 1 uses a dynamic IP address, and DHCP client 2 uses a static IP address.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable DHCP snooping in the system view and an interface view.
Configure trusted and untrusted interfaces to prevent bogus DHCP server attacks.
Configure the DHCP snooping binding table so that the device can check ARP, IP, and DHCP request packets to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks, IP/MAC address spoofing, and attacks by sending bogus DHCP request packets for extending IP address lease.
Enable CHADDR field check to prevent attacks that change CHADDR field values in packets.
Configure Option 82 to create a binding table containing accurate interface information.
Configure the device to report alarms to the Network Management System (NMS).
(Optional) Configure the whitelist function for DHCP snooping.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
ID of the virtual local area network (VLAN) to which the interface belongs
- Threshold of reporting alarms to the NMS
Procedure
- Enable DHCP snooping.
# Enable DHCP snooping globally and for the interface.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DHCP-relay [*HUAWEI] commit [~DHCP-relay] dhcp snooping enable [~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] dhcp snooping enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Configure trusted interfaces.
# Configure the interface connecting to the DHCP server as a trusted interface, and enable DHCP snooping on all the interfaces connecting to the DHCP client. (If the interface on the client side is not configured as a trusted interface, the default interface mode is untrusted after DHCP snooping is enabled on the interface.) This prevents bogus DHCP server attacks.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] dhcp snooping trusted [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Enable packet check and configure the DHCP snooping binding table.
# Configure the device to check Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and IP packets on the interface on the DHCP client side. This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks and IP/MAC address spoofing.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping check arp enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping check ip enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure the device to check DHCP request packets on the interface on the DHCP client side. This prevents attacks in which the attacker sends bogus DHCP request packets for extending IP address lease.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping check dhcp-request enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure the device to check packets containing the CHADDR field on the interface on the DHCP client side. This prevents DoS attacks in which the attacker changes the CHADDR field value.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp check chaddr enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure static DHCP snooping binding table entries.
For users using static IP addresses, static DHCP snooping binding table entries must be manually configured.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping bind-table static ip-address 10.1.3.1 mac-address 00e0-fc5e-008a [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure Option 82 field insertion.
# Enable Option 82 field insertion to set up dynamic binding table entries with accurate interface information.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp option82 insert enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure the device to report alarms to the NMS.
# Enable alarm reporting to the NMS.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-reply enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm arp enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm ip enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure the alarm thresholds.
[~DHCP-relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-reply threshold 10 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm arp threshold 10 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm ip threshold 10 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 10 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 10 [*DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DHCP-relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure the DHCP binding table update function.
# The system performs ARP probing on the IP addresses whose aging time expires in DHCP snooping entries and that do not exist in ARP entries. If the system fails to detect the user after the specified number of attempts, it removes the corresponding binding relationship in the DHCP snooping binding table and instructs the DHCP server to release the user's IP address.
[~DHCP-relay] arp dhcp-snooping-detect enable [*DHCP-relay] commit
- (Optional) Configure the whitelist function for DHCP snooping.
# Create a whitelist.
[~DHCP-relay] dhcp snooping packet whitelist whitelist1# Configure rules for the whitelist.
[*DHCP-relay-dhcpsnp-whitelist-whitelist1] dhcp packet-rule 1 source-ip 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 destination-ip 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 source-port bootpc destination-port bootps [*DHCP-relay-dhcpsnp-whitelist-whitelist1] commit [~DHCP-relay-dhcpsnp-whitelist-whitelist1] quit
# Apply the whitelist.
[~DHCP-relay] dhcp snooping apply packet whitelist whitelist1 [*DHCP-relay] commit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display dhcp snooping global command on the DHCP relay. You can see that DHCP snooping is enabled in the system view and interface view. You can also view the statistics on the alarms sent to the NMS.
[~DHCP-relay] display dhcp snooping global dhcp snooping enable [~DHCP-relay] display dhcp snooping interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping check arp enable dhcp snooping alarm arp enable dhcp snooping alarm arp threshold 10 dhcp snooping check ip enable dhcp snooping alarm ip enable dhcp snooping alarm ip threshold 10 dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-reply enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-reply threshold 10 dhcp check chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 10 dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 10 arp total 0 ip total 0 dhcp-request total 0 chaddr&src mac total 0 dhcp-reply total 0 [~DHCP-relay] display dhcp snooping interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping trusted arp total 0 ip total 0 dhcp-request total 0 chaddr&src mac total 0 dhcp-reply total 0 [~DHCP-relay] display dhcp snooping bind-table static bind-table: ifname vrf/vsi/bdid p/cvlan mac-address ip-address tp lease ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GE0/1/0 -- 0000/0000 00e0-fc5e-008a 010.001.003.001 S 0 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- binditem count: 1 binditem total count: 1 [~DHCP-relay] display dhcp option82 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 dhcp option82 insert enable
Configuration Files
# sysname DHCP-relay # dhcp snooping enable arp dhcp-snooping-detect enable # dhcp snooping packet whitelist whitelist1 dhcp packet-rule 1 source-ip 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 destination-ip 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 source-port bootpc destination-port bootps # dhcp snooping apply packet whitelist whitelist1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select relay ip relay address 10.1.1.2 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping check arp enable dhcp snooping alarm arp enable dhcp snooping alarm arp threshold 10 dhcp snooping check ip enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-reply enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-reply threshold 10 dhcp check chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 10 dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 10 dhcp snooping bind-table static ip-address 10.1.3.1 mac-address 00e0-fc5e-008a dhcp option82 insert enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping trusted # return