DHCP Client
Related Concepts
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) dynamically assigns IP addresses to hosts and centrally manages host configurations. DHCP uses the client/server model. A client applies to the server for configuration parameters, such as an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address; the server replies with the requested configuration parameters.
Usage Scenarios
With the DHCP client function configured, a device uses DHCP to dynamically request an IP address from the DHCP server. This achieves appropriate assignment and centralized management of IP addresses.
Implementation
To obtain a valid dynamic IP address, a DHCP client exchanges different information with the DHCP server at different stages. Generally, the DHCP client and server interact in the following modes:
A DHCP client dynamically obtains an IP address.
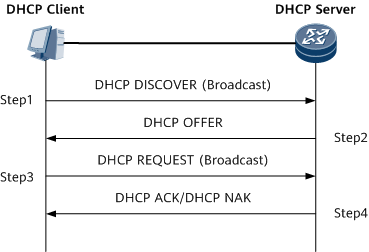
As shown in Figure 1, the DHCP client establishes a connection with the DHCP server through the following four stages:Discovery stage: The DHCP client searches for a DHCP server. The DHCP client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message and only DHCP servers respond to the message.
Offer stage: Each DHCP server offers an IP address to the DHCP client. After receiving the DHCPDISCOVER message from the DHCP client, each DHCP server selects an unassigned IP address from the IP address pool, and sends a DHCPOFFER message with the leased IP address and other configurations to the DHCP client.
Request stage: The DHCP client selects an IP address. If multiple DHCP servers send DHCPOFFER messages to the DHCP client, the DHCP client accepts the first DHCPOFFER message it receives, and broadcasts to each DHCP server a DHCPREQUEST message carrying information about the selected IP address.
- Acknowledgement stage: indicates the stage at which the DHCP server acknowledges the IP address that is offered. When the selected DHCP server receives the DHCP Request message, it searches for a related lease record based on the MAC address or Option 61 field in the received message.
- If the related lease record exists, the DHCP server sends the DHCP client a DHCP ACK message containing the DHCP client's IP address. After receiving the DHCP ACK message, the DHCP client broadcasts a gratuitous ARP message to check whether any host is using the IP address assigned by the DHCP server. If the DHCP client does not receive a response within a specified period, it uses the IP address.
- If the related lease record does not exist or the DHCP server fails to properly assign IP addresses, the DHCP server sends a DHCP NAK message to inform the DHCP client that it cannot assign a proper IP address. In this case, the DHCP client has to send another DHCP Discover message for a new application.
The DHCP client updates the lease period.
Some DHCP clients use a fixed IP address for a long time, and some DHCP clients use a temporary IP address. After a DHCP client's lease time is expired, the DHCP server reclaims the IP address of the DHCP client and allocates this IP address to another DHCP client. You can configure an expected lease time for a DHCP client as required. In this case, while assigning an address lease time, the DHCP server compares the expected lease time with the address lease time of the current address pool and provides the DHCP client an appropriate lease time based on address assignment rules.
After the lease time configured for a DHCP client to obtain a dynamic IP address from the DHCP server is expired, if the DHCP client wants to continue using this IP address, the IP address lease needs to be renewed.
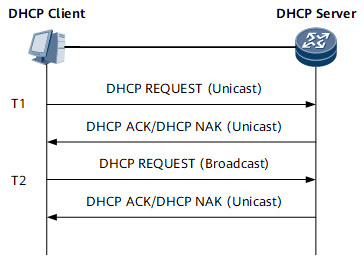
Figure 2 shows how a DHCP client establishes a connection with the DHCP server to update the IP address lease.- When the IP address lease reaches 50% (T1), the DHCP client automatically sends a DHCP Request message in unicast mode to the DHCP server to renew the IP address lease.
- If a DHCP ACK message is received, the IP address lease is successfully renewed.
- If a DHCP NAK message is received, the DHCP client re-initiates the renewal procedure.
- When the IP address lease reaches 87.5% (T2), if the DHCP client has not received a DHCP ACK message yet, it broadcasts a DHCP Request message to DHCP servers to renew its IP address lease.
- If a DHCP ACK message is received, the IP address lease is successfully renewed.
- If a DHCP NAK message is received, the DHCP client re-initiates the renewal procedure.
- If the DHCP client receives no response before the IP address lease expires, the DHCP client stops using the current IP address and sends a DHCP Discover message to request a new IP address.
- When the IP address lease reaches 50% (T1), the DHCP client automatically sends a DHCP Request message in unicast mode to the DHCP server to renew the IP address lease.
The DHCP client proactively releases the IP address.
When the DHCP client no longer uses the assigned IP address, it proactively sends a DHCP Release message to the DHCP server to instruct the server to release the IP address lease. The DHCP server retains the DHCP client's configuration for reuse in case that the client re-applies for an IP address.