(Optional) Configuring DHCP Server Dual-Device Hot Backup
Dual-device hot backup of a DHCP server can be enabled to achieve backup of user session information between devices. When a network node or link experiences an abnormality, fast user service switching is triggered, which enhances service reliability.
Prerequisites
Before configuring DHCP server dual-device hot backup, ensure that the same DHCP server configuration has been performed on the master and slave devices. Otherwise, a master/slave switchover may lead to an abnormality in new user access and user renewal.
The DHCP server function has been enabled using the dhcp server enable command on an interface if the interface needs to be used as a DHCP server.

- If multiple interfaces need to be used as DHCP servers, for security purposes, you are advised to preferentially run the dhcp server enable command on the interfaces to enable the DHCP server function. If high security is not required, you run the dhcp server request-packet all-interface enable command in the system view to enable the DHCP server function for all interfaces.
- If the DHCP server function is not enabled, a DHCP server does not process DHCP request messages.
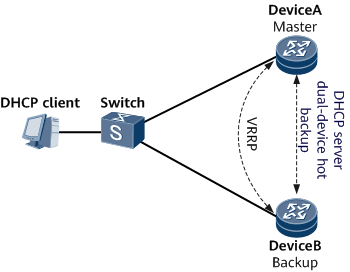
Background
As shown in Figure 1, the DHCP client is connected to DeviceA and DeviceB over a switch. A VRRP group is configured between DeviceA and DeviceB to establish the master/backup relationship, with DeviceA as the master device and DeviceB as the backup device. Both DeviceA and DeviceB serve as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to DHCP clients.
In normal cases, DeviceA implements new user access and online user renewal. When DeviceA or the link between DeviceA and the switch becomes faulty, a master/backup VRRP switchover is implemented and DeviceB takes over to become the master device. DeviceB can properly perform address assignment for new users and renewal requests for online users only when user session information has been synchronized from DeviceA to DeviceB.
To prevent abnormalities of new user access and online user renewal after a master/backup switchover due to a failure to synchronize user session information from DeviceA to DeviceB, deploy DHCP server dual-device hot backup on DeviceA and DeviceB.
Perform the following operations on the DHCP servers that back up each other: