(Optional) Configuring DHCPv6 Relay Dual-Device Hot Standby
DHCPv6 relay dual-device hot standby can be enabled to back up user entries between devices. If a network node or link fails, a rapid user service switchover is triggered, improving service reliability.
Prerequisites
Before configuring DHCPv6 relay dual-device hot standby, complete the following tasks:
- Ensure that the same DHCPv6 relay configurations have been performed on the master and backup devices (the DHCPv6 relay interface types and VLANs configured on the master and backup devices must be the same).
- Ensure that the system time of the master device is the same as that of the backup device (you are advised to configure clock synchronization).
Context
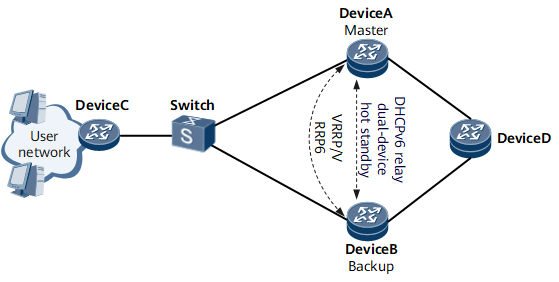
On the network shown in Figure 1, a VRRP or VRRP6 group is configured on DeviceA and DeviceB to establish a master/backup relationship. DeviceA and DeviceB are the master and backup, respectively. Both DeviceA and DeviceB are DHCPv6 relay agents that forward DHCPv6 client and server packets.
In normal situations, DeviceA forwards user packets, and DeviceB receives user entries synchronized from DeviceA and generates PD routes based on the user entries. If DeviceA or the link between DeviceA and the switch fails, a master/backup VRRP or VRRP6 switchover is performed, and DeviceB becomes the master. In this case, user packets are switched to DeviceB for forwarding. Users are unaware of the fault.
Perform the following steps on the DHCPv6 relay agents that back up each other. The following uses a VRRP6 group as an example to describe how to configure DHCPv6 relay dual-device hot standby. The procedure for configuring a VRRP group is similar to that for configuring a VRRP6 group.