Configuring ERPSv2
ERPS eliminates loops on an Ethernet ring network when no faulty links exist and promptly restores communication if a link fault occurs. ERPSv2, compatible with ERPSv1, supports multi-ring topologies and association with CFM, in addition to ERPSv1 functions, such as single ring topologies and multi-instance.
Usage Scenario
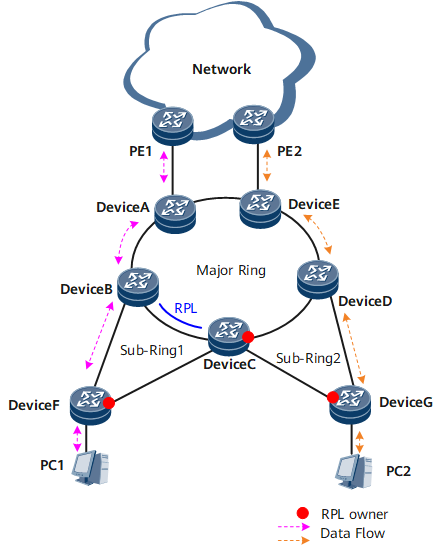
Generally, redundant links are used to access an upper-layer network to provide link backup and enhance network reliability. The use of redundant links, however, may produce loops, causing broadcast storms and rendering the MAC address table unstable. As a result, the communication quality deteriorates, and communication services may even be interrupted. To resolve these problems, ERPS can be used for loop avoidance purposes. ERPS blocks redundant links under normal conditions and unblocks them to promptly restore communication if a link fault occurs. As ERPSv1 supports only single ring topologies, ERPSv2 that supports multi-ring topologies can be used on the multi-ring network shown in Figure 1.

ERPS and other ring network protocols, such as STP and Smart Link, cannot run on the same port.
- Configuring an ERPS Ring
- A ring is the basic ERPS unit. After an ERPS ring is configured, ERPS runs to block redundant links and eliminate loops on Layer 2 networks.
- Configuring Topology Change Notification
- The topology change notification function configured on the interconnection nodes of intersecting ERPS rings allows one ERPS ring to notify the other ERPS rings of its topology change. Then all devices on the other ERPS rings clear their MAC and ARP entries and relearn MAC addresses from the ring with a topology change. This function ensures that user traffic is not interrupted.
- (Optional) Configuring ERPS Protection Switching
- To ensure that ERPS rings function normally when a device or link fails, you can set ERPS protection switching functions, such as revertive and non-revertive switching, port blocking modes, and timers.
- (Optional) Configuring Association Between ERPS and Ethernet CFM
- Association between Ethernet CFM and ERPS on an ERPS ring port helps promptly detect failures, converge topologies, and shorten the traffic interruption time. Currently, ERPS can be associated only with outward-facing MEPs.
- Verifying the ERPSv2 Configuration
- After configuring ERPSv2, verify the configuration of ports added to an ERPS ring, port roles, control VLAN ID, ERP instances, ERPS version, and timers.