Example for Configuring an Eth-Trunk Interface to Work in Static LACP Mode
In the following networking, LACP packets are used to negotiate aggregation parameters to determine the link aggregation modes of active and inactive interfaces. In static LACP mode, you need to manually create an Eth-Trunk interface and add Ethernet interfaces to the Eth-Trunk interface, and LACP selects active and inactive interfaces by negotiating aggregation parameters using LACP packets.
Networking Requirements
You can bundle multiple Ethernet interfaces into a logical Eth-Trunk interface to increase bandwidth, improve link reliability, and implement load balancing. In static LACP mode, member interfaces of the Eth-Trunk interface back up each other dynamically.
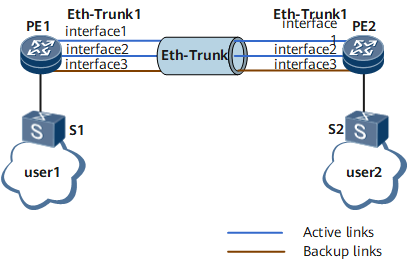
On the network shown in Figure 1, user group 1 communicates with user group 2. You can configure Eth-Trunk interfaces in static LACP mode on PE1 and PE2 to improve the communication quality, implement load balancing, and allow member interfaces to dynamically back up each other.
Precautions
In static LACP mode, the maximum number of active links can be set to control the number of active member interfaces. The number of active member interfaces can reach but cannot exceed the maximum number. When the number of active member interfaces reaches the maximum number, additional active member interfaces are set to Down.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create an Eth-Trunk interface in static LACP mode on each PE and add Ethernet interfaces to the Eth-Trunk interface to implement link aggregation.
- Configure Eth-Trunk interface parameters.
- Configure LACP system priorities for the two Eth-Trunk interfaces to determine the Actor that selects active member interfaces.
- Configure the maximum number of active member links to ensure link bandwidth and improve network reliability.
- Configure LACP preemption and a preemption delay to prevent Eth-Trunk interface flapping caused by frequent status changes of member interfaces. Member interfaces that went Down can switch back to the Selected state to forward traffic only after the preemption delay times out. This ensures reliable data transmission.
Configure parameters for Eth-Trunk member interfaces.
Configure interface LACP priorities for member interfaces to allow interfaces with higher priorities to be selected as active interfaces.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Eth-Trunk interface ID and working mode
LACP system priority of PE1
Maximum number of active links
Delay for LACP preemption
LACP priorities of active interfaces
Procedure
- Create Eth-Trunk 1, configure the Eth-Trunk interface to work in static LACP mode, and add interfaces to the Eth-Trunk interface.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface eth-trunk 1 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] mode lacp-static [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] eth-trunk 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] eth-trunk 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] eth-trunk 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface eth-trunk 1 [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] mode lacp-static [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] eth-trunk 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] eth-trunk 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] eth-trunk 1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure parameters for an Eth-Trunk interface in static LACP mode.
Set the LACP system priority of PE1 to 100 to make it become the Actor.
[~PE1] lacp priority 100 [*PE1] commit
Set the maximum number of active links to 2.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface eth-trunk 1 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] max active-linknumber 2 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface eth-trunk 1 [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] max active-linknumber 2 [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] commit
Enable LACP preemption and set the delay for LACP preemption.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1-Eth-Trunk1] lacp preempt enable [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] lacp preempt delay 20 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] commit [~PE1-Eth-Trunk1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface eth-trunk 1 [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] lacp preempt enable [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] lacp preempt delay 20 [*PE2-Eth-Trunk1] commit [~PE2-Eth-Trunk1] quit
- Configure parameters for Eth-Trunk member interfaces.
# Configure LACP priorities.
# Configure PE1.
[*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] lacp priority 100 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] lacp priority 100 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] lacp priority 150 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] lacp priority 100 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] lacp priority 100 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] lacp priority 150 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*PE2] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Check Eth-Trunk interface information on each PE. You can view the ID and selected member interfaces of the Eth-Trunk interface and find that the Eth-Trunk interface works in static LACP mode.
[~PE1] display eth-trunk 1 Eth-Trunk1's state information is: Local: LAG ID: 1 WorkingMode: STATIC Preempt Delay Time: 20 Hash arithmetic: According to flow System Priority: 100 System ID: 00e0-fc12-3456 Least Active-linknumber: 1 Max Active-linknumber: 16 Operate status: up Number Of Up Ports In Trunk: 2 Timeout Period: Slow -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ActorPortName Status PortType PortPri PortNo PortKey PortState Weight GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Selected 1GE 100 262 561 11111100 1 GigabitEthernet0/1/9 Selected 1GE 100 263 545 11100000 1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 Unselect 1GE 150 264 561 11111100 1 Partner: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ActorPortName SysPri SystemID PortPri PortNo PortKey PortState GigabitEthernet0/1/1 32768 00e0-fc12-3457 100 262 561 11111100 GigabitEthernet0/1/9 32768 00e0-fc12-3457 100 263 545 11100000 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 32768 00e0-fc12-3457 150 264 561 11111100 [~PE2] display eth-trunk 1 Eth-Trunk1's state information is: Local: LAG ID: 1 WorkingMode: STATIC Preempt Delay Time: 20 Hash arithmetic: According to flow System Priority: 32768 System ID: 00e0-fc12-3457 Least Active-linknumber: 1 Max Active-linknumber: 16 Operate status: up Number Of Up Ports In Trunk: 2 Timeout Period: Slow -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ActorPortName Status PortType PortPri PortNo PortKey PortState Weight GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Selected 1GE 100 262 561 11111100 1 GigabitEthernet0/1/9 Selected 1GE 100 263 545 11100000 1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 Unselect 1GE 150 264 561 11111100 1 Partner: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ActorPortName SysPri SystemID PortPri PortNo PortKey PortState GigabitEthernet0/1/1 100 00e0-fc12-3456 100 262 561 11111100 GigabitEthernet0/1/9 100 00e0-fc12-3456 100 263 545 11100000 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 100 00e0-fc12-3456 150 264 561 11111100
The preceding command output shows that the LACP system priority of PE1 is 100, which is higher than the LACP system priority of PE2. Among the member interfaces of the Eth-Trunk interface, Gigabitethernet 0/1/1 and Gigabitethernet 0/1/9 are active interfaces in the Selected state, and Gigabitethernet 0/1/16 is in the Unselected state. In addition, two links carry out load balancing and one link is standby.
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # lacp priority 100 # interface Eth-Trunk1 mode lacp-static security-key cipher *** lacp preempt enable max active-linknumber 2 lacp preempt delay 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 lacp priority 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 lacp priority 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 lacp priority 150 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # interface Eth-Trunk1 mode lacp-static lacp preempt enable max active-linknumber 2 lacp preempt delay 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 lacp priority 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 lacp priority 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 lacp priority 150 # return