In a scenario where multiple CEs are dual-homed to PEs, if you want to use different transmission modes (load balancing and non-load balancing) to send unicast traffic to different CEs or if you want to specify DFs for traffic forwarding by setting priority values, you can set a redundancy mode and DF priority values based on ESIs.
Context
On the network shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE2 are each dual-homed to PE1 and PE2. The PE interfaces that connect to CE1 have ESI 1 (shown in green), and the PE interfaces that connect to CE2 have ESI 2 (shown in blue). If you want CE3-to-CE1 unicast traffic and CE3-to-CE2 unicast traffic to be transmitted in load balancing and non-load balancing modes, respectively, you can set a redundancy mode per ESI instance. Specifically, you can set the redundancy mode of the ESI 1 instance to all-active and that of the ESI 2 instance to single-active.
If you want CE3-to-CE2 BUM traffic to be forwarded by PE1, configure ESI-based DF priority election on PE1 and PE2 and specify PE1 as the primary DF.
Figure 1 Setting a redundancy mode per ESI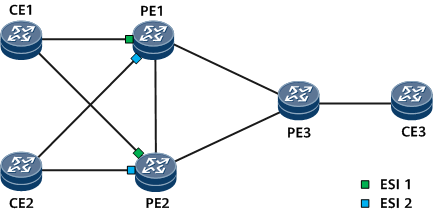
An ESI can be dynamically generated or statically configured. A redundancy mode per ESI instance must be set based on the ESI generation mode.
Procedure
- Set a redundancy mode based on a statically configured ESI.
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run evpn
The global EVPN configuration view is displayed.
- Run esi esi
A static ESI instance name is configured. The esi value must be the same as the name of the statically configured ESI.
- Run evpn redundancy-mode { single-active | all-active }
A redundancy mode is configured for the static ESI instance.
- (Optional) Run df-election type preference-based
Priority-based DF election is enabled.
- (Optional) Run preference preference
A priority value is set. A larger value indicates a higher priority.
- (Optional) Run non-revertive
The non-revertive mode is enabled.
As shown in Figure 1, CE2 is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2. PE1 is elected as the primary DF to forward traffic because it has a higher priority. If PE1 fails, traffic is switched to PE2 for forwarding. After PE1 recovers, traffic is switched back to PE1. To reduce traffic switching times and maintain service topology stability, run the non-revertive command to disable traffic switchback.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Set a redundancy mode based on a dynamically generated ESI.
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run evpn
The global EVPN configuration view is displayed.
- Run esi dynamic-name esi-name
A dynamic ESI instance name is configured.
- Run evpn redundancy-mode { single-active | all-active }
A redundancy mode is configured for the dynamic ESI instance.
- (Optional) Run df-election type preference-based
Priority-based DF election is enabled.
- (Optional) Run preference preference
A priority value is set. A larger value indicates a higher priority.
- (Optional) Run non-revertive
The non-revertive mode is enabled.
As shown in Figure 1, CE2 is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2. PE1 is elected as the primary DF to forward traffic because it has a higher priority. If PE1 fails, traffic is switched to PE2 for forwarding. After PE1 recovers, traffic is switched back to PE1. To reduce traffic switching times and maintain service topology stability, run the non-revertive command to disable traffic switchback.
- Run quit
Return to the ESI-dynamic view.
- Run quit
Return to the global EVPN configuration view.
- Run quit
Return to the system view.
- Run interface eth-trunk trunk-id
The Eth-Trunk interface view is displayed.
- Run esi dynamic esi-name
A dynamic ESI instance is bound to the Eth-Trunk interface.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
