Configuring the NFVI Distributed Gateway Function (BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 over E2E SR Tunnels)
In the NFVI telco cloud solution, the NFVI distributed gateway function allows mobile phone traffic to be processed by vUGWs and vMSEs and transmitted over a DCN through E2E SR tunnels as well as being transmitted within a DCN in load balancing mode.
Usage Scenario
The NFVI telco cloud solution uses the DCI+DCN networking. A large amount of mobile phone traffic is sent to vUGWs and vMSEs on the DCN. After being processed by the vUGWs and vMSEs, the mobile phone traffic is forwarded over the DCN to destination devices on the Internet. The destination devices send traffic to mobile phones in similar ways. To achieve these functions and ensure traffic load balancing on the DCN, you need to deploy the NFVI distributed gateway function.
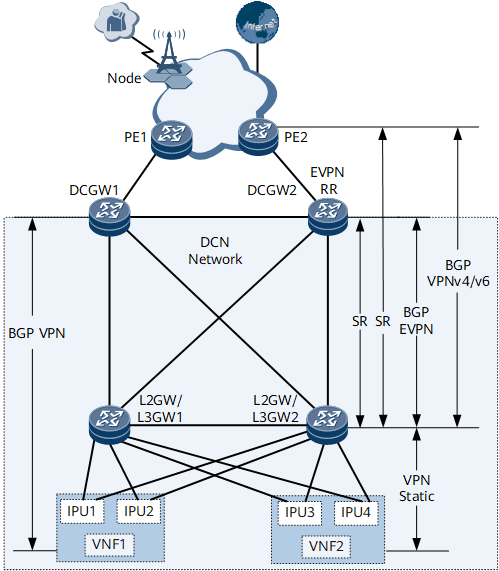
Figure 1 shows the networking of an NFVI distributed gateway (BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 over E2E SR tunnels). DC-GWs, which are the border gateways of the DCN, exchange Internet routes with external devices over PEs. L2GW/L3GW1 and L2GW/L3GW2 are connected to VNFs. VNF1 and VNF2 that function as virtualized NEs are deployed to implement the vUGW functions and vMSE functions, respectively. VNF1 and VNF2 are each connected to L2GW/L3GW1 and L2GW/L3GW2 through IPUs.
Establish BGP VPN peer relationships between VNFs and DC-GWs so that the VNFs can advertise mobile phone routes (UE IP) to DC-GWs.
On L2GW/L3GW1 and L2GW/L3GW2, configure static VPN routes with the IP addresses of VNFs as the destination addresses and the IP addresses of IPUs as next-hop addresses.
Establish BGP EVPN peer relationships between any DC-GW and L2GW/L3GW. The DC-GW can then advertise local loopback routes and default routes to the L2GW/L3GW. A route-policy needs to be configured on DC-GWs so that the routes sent by DC-GWs to L2GW/L3GWs carry gateway addresses and the next hops of the mobile phone routes received by L2GW/L3GWs from DC-GWs are the VNF addresses. In addition, the BGP EVPN peer relationships established between DC-GWs and L2GW/L3GWs can be used to advertise the routes carrying the IP addresses used for establishing BGP VPN peer relationships, and the BGP EVPN peer relationships established between L2GW/L3GWs can be used to synchronize the MAC or ARP routes and the IP prefix routes carrying gateway addresses with IPUs.
Deploy EVPN RRs which can be either a standalone device or a DC-GW. In this section, DC-GWs function as EVPN RRs, and L2GW/L3GWs function as RR clients. L2GW/L3GWs can use EVPN RRs to synchronize MAC or ARP routes as well as the IP prefix routes carrying a VNF address as the destination address with IPUs.
Establish BGP VPNv4/v6 peer relationships between L2GW/L3GWs and PEs. L2GW/L3GWs advertise mobile phone routes to PEs based on BGP VPNv4/v6 peer relationships. DC-GWs send mobile phone routes to L2GW/L3GWs based on BGP EVPN peer relationships. Therefore, mobile phone routes need to be re-encapsulated as BGP VPNv4/v6 routes on L2GW/L3GWs before being advertised to PEs.
Configure static default routes on PEs and configure the PEs to send static default routes to L2GW/L3GWs based on BGP VPNv4/v6 peer relationships.
Deploy SR tunnels between PEs and L2GW/L3GWs and between DC-GWs and L2GW/L3GWs to carry service traffic.
The traffic transmitted between mobile phones and the Internet over VNFs is north-south traffic. The traffic transmitted between VNF1 and VNF2 is east-west traffic. To achieve load balancing of east-west traffic and north-south traffic, deploy the load balancing function on DC-GWs and L2GW/L3GWs.

The NFVI distributed gateway function supports both IPv4 and IPv6 services. If a step does not differentiate IPv4 and IPv6 services, this step applies to both IPv4 and IPv6 services.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring the NFVI distributed gateway function, complete the following tasks:
Allow the routes between PEs and DC-GWs and between DC-GWs and L2GW/L3GWs to be reachable.
Deploy SR tunnels between PEs and L2GW/L3GWs and between DC-GWs and L2GW/L3GWs.
Configure the BD EVPN function on DC-GWs and L2GW/L3GWs. The configuration includes creating EVPN instances and L3VPN instances, establishing BGP EVPN peer relationships, and configuring VBDIF interfaces. On DC-GWs, the configuration involves only creating L3VPN instances and establishing BGP EVPN peer relationships.
Deploy L3VPN instances on PEs, and EBGP VPNv4 or EBGP VPNv6 has been deployed between PEs and L2GW/L3GWs.
Configure the static routes destined for VNF1 and VNF2 on L2GW/L3GWs by referring to Static VPN IPv4 Routes or Static VPN IPv6 Routes.
- Configuring Route Recursion over SR Tunnels
- By default, routes are recursed to a BD EVPN or BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 network over MPLS LDP tunnels. If SR tunnels are used to carry service traffic, the function to recurse routes over SR tunnels must be configured.
- Configuring Route Advertisement on PEs
- The route advertisement allows PEs to advertise default static routes to L2GW/L3GWs based on BGP VPNv4 peer relationships.
- Configuring Route Advertisement on DC-GWs
- Route advertisement can be configured on DC-GWs to allow the DC-GWs to construct their own forwarding entries based on the received EVPN or BGP routes.
- Configuring Route Advertisement on L2GW/L3GWs
- Route advertisement can be configured on L2GW/L3GWs to allow the L2GW/L3GWs to construct their own forwarding entries based on the received EVPN or BGP routes.
- Configuring the Load Balancing Function
- The load balancing function needs to be deployed to achieve balanced loads of network traffic.
- Verifying the Configurations of the NFVI DistributedGateway Function
- After configuring the NFVI distributed gateway function, verify the configurations. On DC-GWs, you can view the VPN peer relationships between DC-GWs and VNFs and the information about the mobile phone routes received from VNFs.