Setting a Delay in Releasing an Obtained Label in a BGP EVPN FRR Switchover Scenario
After you set a delay in releasing an obtained label in a BGP EVPN FRR switchover scenario, you can prevent second-time packet loss.
Usage Scenario
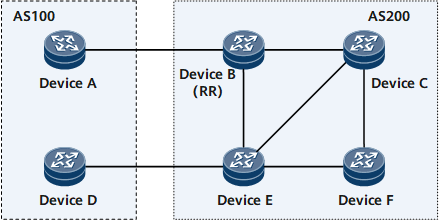
As shown in Figure 1, Device A and Device D belong to AS100, and Device B, Device C, Device E, and Device F belong to AS200 in a BGP EVPN FRR switchover scenario. Device B selects the optimal route that is learned from the EBGP EVPN peer Device A and the sub-optimal route that is learned from the IBGP EVPN peer Device E. In normal situations, Device B preferentially selects a labeled BGP route learned from EBGP EVPN peer Device A and advertises the route to the IBGP EVPN peer Device C. Device B delivers an incoming label map (ILM) entry and next hop label forwarding entry (NHLFE), and Device C also delivers an NHLFE entry. If Device A is restarted due to a fault, Device B withdraws the route learned from Device A, selects the sub-optimal route learned from IBGP EVPN peer Device E, and reflects the route to Device C through the RR. Then, Device B releases the applied label and deletes the ILM entry mapped to the label. If traffic arrives at Device C before Device C updates the NHLFE entry, Device C still uses this entry to forward traffic to Device B. Because Device B has released the label and deleted the ILM entry, packets are lost for the second time.
To prevent traffic loss during a BGP EVPN FRR switchover, configure the local device to delay deleting the ILM entry.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before setting a delay in releasing an obtained label in a BGP EVPN FRR switchover scenario, complete the following tasks:
Configure BGP Auto FRR in the BGP-EVPN address family view.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bgp { as-number-plain | as-number-dot }
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run l2vpn-family evpn
The BGP-EVPN address family view is displayed.
- Run label-free delay delay-value
A delay time in releasing obtained labels is set.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Verifying the Configuration
After setting a delay in releasing an obtained label in a BGP EVPN FRR switchover scenario, verify the configuration.
Run the display current-configuration command to check the current configuration.