IETF-NACM
Overview
The IETF NETCONF Access Control Model (IETF-NACM) provides simple and easy-to-configure database access control rules. It helps flexibly manage a specific user's permissions to perform NETCONF operations and access NETCONF resources.
The YANG model defines IETF-NACM in the ietf-netconf-acm.yang file.
Protocol operation authentication: authorizes users to perform specific NETCONF operations.
For example, <get>, <get-config>, <edit-config>, <copy-config>, <delete-config>, and <lock>.
Module authorization: authorizes users to access specific feature modules.
Data node authorization: authorizes users to query and modify specific data nodes.
Notification authentication: authorizes a system to report specified alarms or events through the notification mechanism.
- Action authorization: authorizes users to define operations for data nodes through "action" statements.
Emergency session recovery: authorizes users to directly initialize or repair the IETF-NACM authentication configuration without the restriction of access control rules.
Emergency session recovery is a process in which a management-level user or a user in the manage-ug group bypasses the access control rule and initializes or repairs the IETF-NACM authentication configuration.
Management-level users are at Level 3 or 15.

By default, IETF-NACM authentication is disabled and the HUAWEI-NACM authentication process is experienced. If IETF-NACM authentication is enabled, the IETF-NACM authentication process is experienced.
If IETF-NACM authentication is enabled, the access permission on get/ietf-yang-library must be enabled during session establishment. Otherwise, session establishment fails due to no permission.
Data Node Access
The access control permissions of IETF-NACM apply only to NETCONF databases (<candidate/>, <running/>, and <startup/>). The local or remote file or database accessed using the <url> parameter is not controlled by IETF-NACM.
- Create: allows a client to add new data nodes to a database.
- Read: allows a client to read a data node from a database or receive notification events.
- Update: allows a client to update existing data nodes in a database.
- Delete: allows a client to delete a data node from a database.
- Exec: allows a client to perform protocol operations.

Authentication is performed only for the delivered operations but not for all the changed nodes in the model tree. For example, when a delete operation is performed for a parent node, this operation automatically applies to its child nodes without authentication. Therefore, the data of both the parent node and its child nodes is deleted in this case.
Components of IETF-NACM
Table 1 describes the components and functions of IETF-NACM.
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
User |
User defined in the NACM view. The user must be an SSH user. IETF-NACM authenticates users only. User authentication is implemented in the AAA view. |
Group |
Group defined in the NACM view. This group instead of a user performs protocol operations in a NETCONF session. The group identifier is a group name, which is unique on the NETCONF server. Different groups can contain the same user. |
Global execution control |
Execution control can be:
|
Access control rule |
There are five access control rules:
|
Implementation Principles
After a NETCONF session is established and a user passes the authentication, the NETCONF server controls access permissions based on the user name, group name, and NACM authentication rule list. Authentication rules are associated with users through the user group. The administrator of a user group can manage the permissions of users in the group.
- An IETF-NACM user is associated with an IETF-NACM user group. After IETF-NACM users are added to a user group, the users in the same user group have the same permissions.
- An IETF-NACM user group is associated with an IETF-NACM authentication rule list.
An IETF-NACM authentication rule list is associated with IETF-NACM authentication rules.
An IETF-NACM authentication rule list is a set of rules. Various authentication rules can be added to an IETF-NACM authentication rule list in the format of combinations. Users associated with the list can use the rules in it.
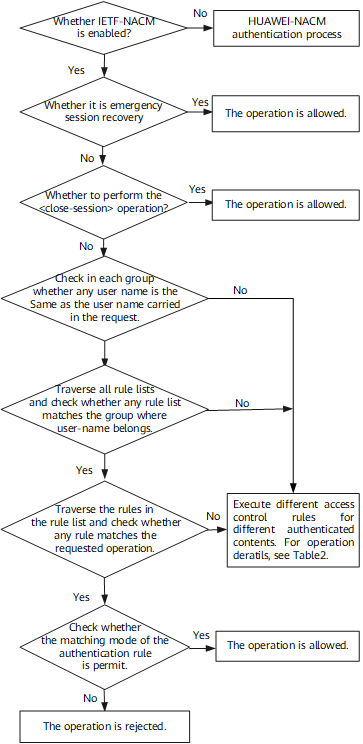
IETF-NACM Authentication Process
Figure 1 shows the IETF-NACM authentication process.
When a user group and an authentication rule list are traversed, if the user name that is the same as that carried in the request is not found or no rule that matches the requested operation is detected, the operation performed varies with the authenticated content. For details, see Table 2.
Authenticated Content |
Operation |
|---|---|
Protocol operation |
|
Data node |
|
Notification |
|
Action |
|