Example for Configuring OSPF GTSM
This section describes how to configure OSPF GTSM to protect devices on an OSPF network against CPU utilization-based attacks.
Networking Requirements
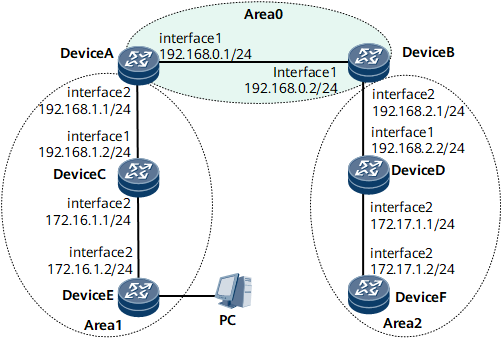
As shown in Figure 1, OSPF runs on the routers and the GTSM is enabled on Device C.
The valid TTL ranges of the packets sent from each router to Device C are as follows:
Device A and Device E are the neighbors of Device C. The valid TTL range of the packets from Device A and Device E to Device C is 255.
The valid TTL ranges of the packets sent from Device B, Device D, and Device F to Device C are [254, 255], [253, 255], and [252, 255] respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic OSPF functions.
Enable the GTSM on each router and specify the valid TTL range of packets.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
OSPF process ID of each router
Valid TTL range of the packets transmitted between the routers
Procedure
- Configure IP addresses for interfaces. The configuration details are not mentioned here.
- Configure the basic OSPF functions. The configuration details are not mentioned here.
- Configure the OSPF GTSM.
# Configure the valid TTL range of the packet from Device C to other routers as [252, 255].
[~DeviceC] ospf valid-ttl-hops 4 [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure the valid TTL range of the packets from Device A to Device C as [255, 255].
[~DeviceA] ospf valid-ttl-hops 1 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure the valid TTL range of the packets from Device B to Device C as [254, 255].
[~DeviceB] ospf valid-ttl-hops 2 [*DeviceB] commit
# Configure the valid TTL range of the packets from Device D to Device C as [253, 255].
[~DeviceD] ospf valid-ttl-hops 3 [*DeviceD] commit
# Configure the valid TTL range of the packets from Device E to Device C as [255, 255].
[~DeviceE] ospf valid-ttl-hops 1 [*DeviceE] commit
# Configure the valid TTL range of the packets from Device F to Device C as [252, 255].
[~DeviceF] ospf valid-ttl-hops 4 [*DeviceF] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Check whether OSPF neighbor relationships between the routers are established normally. Take Device A as an example. You can view the status of the neighbor relationship is Full, that is, neighbors are established normally.
[~DeviceA] display ospf peer OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 1.1.1.1 Neighbors Area 0.0.0.0 interface 192.168.0.1(GigabitEthernet0/1/0)'s neighbors Router ID: 2.2.2.2 Address: 192.168.0.2 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Master Priority: 1 DR: None BDR: None MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 36 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 00:15:04 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ] Neighbors Area 0.0.0.1 interface 192.168.1.1(GigabitEthernet0/1/8)'s neighbors Router ID: 3.3.3.3 Address: 192.168.1.2 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Master Priority: 1 DR: None BDR: None MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 39 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 00:07:32 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ]
# Run the display gtsm statistics all command on Device C. You can view the statistics about the GTSM. If the default action that is performed on the packets is "pass" and all the packets are valid, no packet is dropped.
<DeviceC> display gtsm statistics all GTSM Statistics Table ---------------------------------------------------------------- SlotId Protocol Total Counters Drop Counters Pass Counters ---------------------------------------------------------------- 1 BGP 0 0 0 1 BGPv6 0 0 0 1 OSPF 0 0 0 1 LDP 0 0 0 1 OSPFv3 0 0 0 1 RIP 0 0 0 2 BGP 0 0 0 2 BGPv6 0 0 0 2 OSPF 0 0 0 2 LDP 0 0 0 2 OSPFv3 0 0 0 2 RIP 0 0 0 3 BGP 0 0 0 3 BGPv6 0 0 0 3 OSPF 0 0 0 3 LDP 0 0 0 3 OSPFv3 0 0 0 3 RIP 0 0 0 4 BGP 0 0 0 4 BGPv6 0 0 0 4 OSPF 0 0 0 4 LDP 0 0 0 4 OSPFv3 0 0 0 4 RIP 0 0 0 5 BGP 0 0 0 5 BGPv6 0 0 0 5 OSPF 0 0 0 5 LDP 0 0 0 5 OSPFv3 0 0 0 5 RIP 0 0 0 7 BGP 0 0 0 7 BGPv6 0 0 0 7 OSPF 0 0 0 7 LDP 0 0 0 7 OSPFv3 0 0 0 7 RIP 0 0 0 ----------------------------------------------------------------
If the host PC simulates OSPF packets of Device A to attack Device C, the packets are dropped because the TTL value is not 255 when the packets reach Device C. In the GTSM statistics on Device C, the number of dropped packets also increases.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # router id 1.1.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0.0.0.1 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf valid-ttl-hops 1 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # router id 2.2.2.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0.0.0.2 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf valid-ttl-hops 2 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # router id 3.3.3.3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.1 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf valid-ttl-hops 4 # return
Device configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # router id 4.4.4.4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.2 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.17.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf valid-ttl-hops 3 # return
Device E configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # router id 5.5.5.5 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.1 network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf valid-ttl-hops 1 # return
Device F configuration file
# sysname DeviceF # router id 6.6.6.6 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 172.17.1.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.2 network 172.17.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ospf valid-ttl-hops 4 # return