Overview
This section illustrates why the Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) and GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) are necessary.
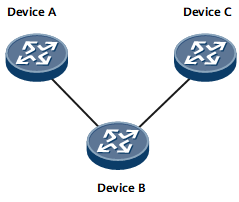
Generally, VLANs are manually created on devices. In Figure 1, Device A and Device C connect to Device B through trunk links. VLAN 2 is created on Device A, and VLAN 1 exists on Device B and Device C by default. To allow packets belonging to VLAN 2 on Device A to be transmitted to Device C over Device B, the network administrator must manually create VLAN 2 on Device B and Device C, a simple task considering this networking.
If the networking is so complicated that the network administrator cannot ascertain the topology in a short time or if numerous VLANs require configuring, the VLAN configuration is time-consuming, and misconfiguration may occur.
GVRP reduces the heavy VLAN configuration workload by completing VLAN configuration through automatic VLAN registration.
After GVRP is enabled, the device can receive VLAN registration information of other devices and dynamically update the local VLAN registration information. In addition, the device can transmit local VLAN registration information to other devices to ensure VLAN information consistency among all devices on the LAN. The VLAN registration information for GVRP includes both the locally configured static registration information and the dynamic registration information received from other devices.