Example for Configuring L3VPNv4 over IPsec over SRv6 BE
Networking Requirements
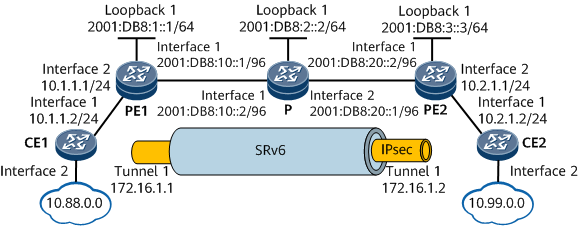
On the network shown in Figure 1:
PE1, the P, and PE2 belong to the same AS and run IS-IS to implement IPv6 network connectivity.
PE1, the P, and PE2 are Level-1 devices and belong to IS-IS process 1.
It is required that a bidirectional SRv6 BE path be established between PE1 and PE2 to carry L3VPNv4 services. In addition, an IPsec tunnel needs to be established between PE1 and PE2. Then CE1 and CE2 can communicate with each other across the SRv6 network.

Interface 1 and interface 2 in this example represent GE 0/1/1 and GE 0/1/2, respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable IPv6 forwarding and configure an IPv6 address for each involved interface on PE1, the P, and PE2.
Enable IS-IS, configure an IS-IS level, and specify a NET on PE1, the P, and PE2.
Configure a VPN instance on PE1 and PE2.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
Configure an SRv6 SID and IS-IS SRv6 and enable VPN routes to carry the SID attribute on PE1 and PE2.
- Define data flows to be protected on PE1 and PE2.
- Configure an IKE proposal on PE1 and PE2.
- Create a tunnel interface on PE1 and PE2.
- Configure an IKE peer on PE1 and PE2.
- Configure an IPsec proposal on PE1 and PE2.
- Configure an IPsec policy on PE1 and PE2.
- Configure an IPsec service instance group on PE1 and PE2.
- Apply the IPsec policy to the tunnel interface on PE1 and PE2.
- Configure a static route on PE1 and PE2 to direct the data flows to be protected to the IPsec tunnel.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IPv6 addresses of interfaces on PE1, the P, and PE2
IS-IS process ID of PE1, the P, and PE2
IS-IS level of PE1, the P, and PE2
VPN instance name, RD, and RTs on PE1 and PE2
- IKE proposal number, authentication algorithm, encryption algorithm, Diffie-Hellman group identifier, and integrity algorithm on PE1 and PE2
- IKE peer name and pre-shared key on PE1 and PE2
- IPsec proposal name, ESP authentication algorithm, and ESP encryption algorithm on PE1 and PE2
- IPsec policy name on PE1 and PE2
- Name of the IPsec service instance group on PE1 and PE2
Procedure
- Configure PE1 and PE2.
Step
PE1
PE2
1. Enable the IPv6 forwarding capability on each involved interface and configure IPv6 addresses for the interfaces.
sysname PE1 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:10::1 96 # interface LoopBack 1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1 64sysname PE2 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:20::2 96 # interface LoopBack 1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::3 642. Configure IS-IS.
isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface LoopBack 1 isis ipv6 enable 1isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface LoopBack 1 isis ipv6 enable 13. Configure a VPN instance enabled with the IPv4 address family.
ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 vpn-target 111:1 both # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.1 24ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 111:1 both # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.2.1.1 244. Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each PE and its connected CE.
bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65410 import-route direct
bgp 100 router-id 3.3.3.3 ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 65420 import-route direct
5. Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the PEs.
bgp 100 peer 2001:DB8:3::3 as-number 100 peer 2001:DB8:3::3 connect-interface loopback 1 ipv4-family vpnv4 peer 2001:DB8:3::3 enable
bgp 100 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 as-number 100 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 connect-interface loopback 1 ipv4-family vpnv4 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 enable
6. Configure an SRv6 SID and IS-IS SRv6, and enable VPN routes to carry the SID attribute.
segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2001:DB8:1::1 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 2001:DB8:100:: 64 static 32 # bgp 100 ipv4-family vpnv4 peer 2001:DB8:3::3 prefix-sid ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna segment-routing ipv6 best-effort segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # isis 1 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1
segment-routing ipv6 encapsulation source-address 2001:DB8:3::3 locator as1 ipv6-prefix 2001:DB8:300:: 64 static 32 # bgp 100 ipv4-family vpnv4 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 prefix-sid ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna segment-routing ipv6 best-effort segment-routing ipv6 locator as1 # isis 1 segment-routing ipv6 locator as1
8. Define data flows to be protected.
acl number 3000 rule 5 permit ip source 10.88.0.0 0.0.0.255 destination 10.99.0.0 0.0.0.255
acl number 3000 rule 5 permit ip source 10.99.0.0 0.0.0.255 destination 10.88.0.0 0.0.0.255
9. Configure an IKE proposal numbered 100.
ike proposal 100 encryption-algorithm aes-cbc 256 dh group14 authentication-algorithm sha2-256 integrity-algorithm hmac-sha2-256
ike proposal 100 encryption-algorithm aes-cbc 256 dh group14 authentication-algorithm sha2-256 integrity-algorithm hmac-sha2-256
10. Create a tunnel interface.
interface Tunnel1 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.255
interface Tunnel1 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.255
11. Configure an IKE peer named srv6.
ike peer srv6 pre-shared-key cipher %^%#Rd&]3,a-N6+k[S;6B)"Hl0zgU%^%# ike-proposal 100 remote-address vpn-instance vpna 172.16.1.2
ike peer srv6 pre-shared-key cipher %^%#M3{(W:`{'L&6_cTideDGSJI+0%^%# ike-proposal 100 remote-address vpn-instance vpna 172.16.1.112. Configure an IPsec proposal named srv6.
ipsec proposal srv6 transform esp esp authentication-algorithm sha2-256 esp encryption-algorithm aes 256 encapsulation-mode tunnel
ipsec proposal srv6 transform esp esp authentication-algorithm sha2-256 esp encryption-algorithm aes 256 encapsulation-mode tunnel
13. Configure an IPsec policy named srv6.
ipsec policy srv6 1 isakmp security acl 3000 ike-peer srv6 proposal srv6
ipsec policy srv6 1 isakmp security acl 3000 ike-peer srv6 proposal srv6
14. Configure an IPsec service instance group.
service-location 1 location slot 1 # service-instance-group 1 service-location 1service-location 1 location slot 1 # service-instance-group 1 service-location 115. Apply the IPsec policy srv6 to the tunnel interface.
interface Tunnel1 tunnel-protocol ipsec ipsec policy srv6 service-instance-group 1
interface Tunnel1 tunnel-protocol ipsec ipsec policy srv6 service-instance-group 1
16. Configure a static route to direct the data flows to be protected to the IPsec tunnel.
ip route-static 10.99.0.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 172.16.1.2
ip route-static 10.88.0.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 172.16.1.1
- Configure the P.
Step
P
1. Enable the IPv6 forwarding capability on each involved interface and configure IPv6 addresses for the interfaces.
sysname P # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:10::2 96 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:20::1 96 # interface LoopBack 1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2 64
2. Configure IS-IS.
isis 1 is-level level-1 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface LoopBack 1 isis ipv6 enable 1
- Configure CE1 and CE2.
Step
CE1
CE2
1. Configure IPv4 addresses.
sysname CE1 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 ip address 10.88.0.1 255.255.255.0
sysname CE2 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 ip address 10.99.0.1 255.255.255.0
2. Establish an EBGP peer relationship between each CE and its connected PE.
bgp 65410 router-id 11.11.11.11 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 100 network 10.88.0.0 255.255.255.0
bgp 65420 router-id 22.22.22.22 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 100 network 10.99.0.0 255.255.255.0