Overview of IPv6 User-Side Multicast
This section describes the definition and purpose of IPv6 user-side multicast.
Definition
IPv6 User-side multicast enables a BRAS to identify users of a multicast program.
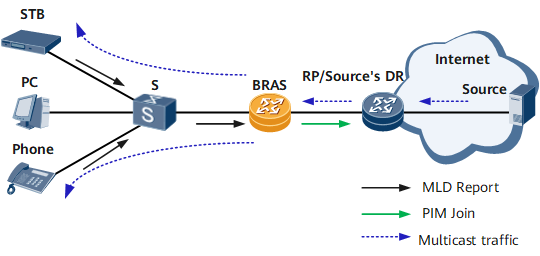
In Figure 1, when the set top box (STB) and phone users go online, they send Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Report messages of a multicast program to the BRAS. After receiving the messages, the BRAS identifies the users and sends a Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Join message to the network-side rendezvous point (RP) or the source's designated router (DR). The RP or source's DR creates multicast forwarding entries for the users and receives the required multicast traffic from the source. The BRAS finally sends the multicast traffic to the STB and phone users based on their forwarding entries and replication modes. The multicast replication in this example is based on sessions.

On Layer 2, user-side multicast supports the PPPoE and IPoE access modes for common users and the IPoE access mode for E-Line users.
Purpose
Because conventional IPv6 multicast does not provide a method to identify users, carriers cannot effectively manage multicast users who access services such as Internet Protocol television (IPTV). Such users can join multicast groups, without notification, by sending MLD Report messages. To identify these users and allow for improved management of them, Huawei provides the IPv6 user-side multicast feature.