Example for Configuring an Inbound LDP Policy
This example describes how to configure an inbound LDP policy. The configuration procedure includes operations of enabling MPLS and MPLS LDP globally.
Networking Requirements
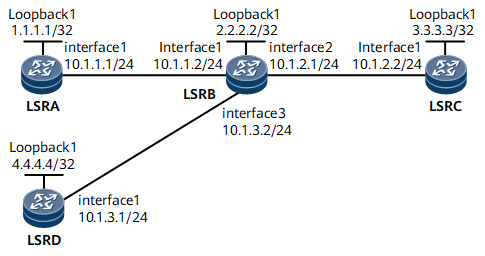
MPLS LDP services are transmitted on the network shown in Figure 1. LSRD is a DSLAM that is a low-performance access device. LSRD by default receives Label Mapping messages from all peers and uses the routing information in these messages to establish a large number of LSPs. As a result, memory on LSRD is overused and LSRD is overburdened. An inbound LDP policy can be configured to allow LSRD to receive only Label Mapping messages for routes to LSRC. Only an LSP originating from LSRD and destined for LSRC can be established, efficiently using resources.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address and a loopback address to each interface.
Configure OSPF to advertise the route to each network segment of each interface and to advertise the host route to each LSR ID.
Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP on each LSR and its interfaces.
Configure an inbound LDP policy.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP address of every interface on every LSR shown in Figure 1, OSPF process IDs, and OSPF area IDs
LSR ID of every LSR
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface and configure an IGP.
Assign an IP address and its mask to every physical interface; configure a loopback interface address as an LSR ID on every LSR shown in Figure 1; configure OSPF to advertise the route of the network segment of each interface and a host rout to each LSR ID. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP on each LSR and its interfaces.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*LSRA] mpls [*LSRA-mpls] quit [*LSRA] mpls ldp [*LSRA-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRA] commit
# Configure LSRB.
[~LSRB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*LSRB] mpls [*LSRB-mpls] quit [*LSRB] mpls ldp [*LSRB-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*LSRB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*LSRB-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*LSRB] commit
# Configure LSRC.
[~LSRC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*LSRC] mpls [*LSRC-mpls] quit [*LSRC] mpls ldp [*LSRC-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRC] commit
# Configure LSRD.
[~LSRD] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4 [*LSRD] mpls [*LSRD-mpls] quit [*LSRD] mpls ldp [*LSRD-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*LSRD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*LSRD] commit
# After completing the preceding configurations, run the display mpls lsp command on LSRD to view information about the established LSPs.
[~LSRD] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.1/32 NULL/32829 -/GE0/1/0 1.1.1.1/32 32828/32829 -/GE0/1/0 2.2.2.2/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/0 2.2.2.2/32 32829/3 -/GE0/1/0 3.3.3.3/32 NULL/32830 -/GE0/1/0 3.3.3.3/32 32830/32830 -/GE0/1/0 4.4.4.4/32 3/NULL -/-
The command output shows that LSPs to LSRA, LSRB, and LSRC have been established on LSRD.
- Configure an inbound LDP policy.
# Configure an IP prefix list on LSRD to permit the routes only to LSRC to pass the inbound LDP policy.
[~LSRD] ip ip-prefix prefix1 permit 3.3.3.3 32 [*LSRD] commit
# Configure an inbound policy on LSRD to allow LSRD to receive Label Mapping messages for the routes only to LSRC.
[~LSRD] mpls ldp [*LSRD-mpls-ldp] ipv4-family [*LSRD-mpls-ldp-ipv4] inbound peer 2.2.2.2 fec ip-prefix prefix1 [*LSRD-mpls-ldp-ipv4] quit [*LSRD-mpls-ldp] quit [*LSRD] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the preceding configurations, run the display mpls lsp command on LSRD. The command output shows that only an LSP to LSRC has been established.
[~LSRD] display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 3.3.3.3/32 NULL/32830 -/GE0/1/0 3.3.3.3/32 32830/32830 -/GE0/1/0 4.4.4.4/32 3/NULL -/-
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Pos1/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface NULL0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
LSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Pos1/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Pos1/0/1 ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Pos1/0/2 ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface NULL0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Pos1/0/0 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface NULL0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
LSRD configuration file
# sysname LSRD # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 mpls # mpls ldp inbound peer 2.2.2.9 fec ip-prefix prefix1 # interface Pos1/0/0 ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface NULL0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # ip ip-prefix prefix1 index 10 permit 3.3.3.9 32 # return