Support for the Creation of a Primary mLDP P2MP LSP in the Class-Specific Topology
This section describes the creation of an mLDP P2MP master tree in the class-specific topology.
Background
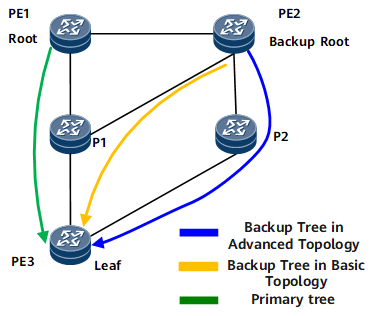
Both NG MVPN over mLDP P2MP and VPLS over mLDP P2MP provide dual-root 1+1 protection. If an mLDP P2MP master tree fails, traffic rapidly switches to a backup tree, which reduces service traffic loss.
mLDP P2MP searches a unicast routing table created in the base topology for root routes, which may cause a protection failure. If unicast routes from the two roots to a leaf node partially overlap and the overlapping link fails, dual-root 1+1 protection fails. Adjusting the unicast routes to prevent a protection failure stemming from an overlapping link but adversely affects existing unicast services.
An apparent solution is to divide a physical network into different logical topologies for different services. This is called multi-topology. Each class-specific topology in a public network address family contains an independent routing table. The class-specific topology allows protocol routes to be added, deleted, and imported. Based on the multi-topology and class-specific topology, the class-specific topology can be configured to address the dual-root 1+1 protection failure for mLDP P2MP tunnels.
mLDP P2MP is a typical application of the class-specific topology. A primary mLDP P2MP LSP can be configured in the class-specific topology. Routes then only partially depend on the unicast routing table. Route priorities can be adjusted in the class-specific topology to prevent the overlapping link, which does not affect unicast services.

Basic Concepts
- Base topology: is created by default on a public network and cannot be configured or deleted.
- Class-specific topology: can be added, deleted, or imported.
Implementation
Benefits
Deployment can be modified to prevent mLDP P2MP dual-root 1+1 protection failures stemming from the overlapping link issue, without unicast services affected.