Overview of LLDP
LLDP provides a standard link-layer discovery method to encapsulate information about the capabilities, management address, device ID, and interface ID of a local device into LLDP packets. These packets are sent to neighboring devices that save the information received in a standard Management Information Base (MIB) to help the NMS query and determine the communication status of links.
Background
Diversified network devices are deployed on a network, and configurations of these devices are complicated. Therefore, NMSs must be able to meet increasing requirements for network management capabilities, such as the capability to automatically obtain the topology status of connected devices and the capability to detect configuration conflicts between devices. A majority of NMSs use an automated discovery function to trace changes in the network topology, but most can only analyze the network layer topology. Network layer topology information notifies you of basic events, such as the addition or deletion of devices, but gives you no information about the interfaces to connect a device to other devices. The NMSs can identify neither the device location nor the network operation mode.
LLDP is developed to resolve these problems. LLDP can identify interfaces on a network device and provide detailed information about connections between devices. LLDP can also display information about paths between clients, switches, routers, application servers, and network servers, which helps you efficiently locate network faults.
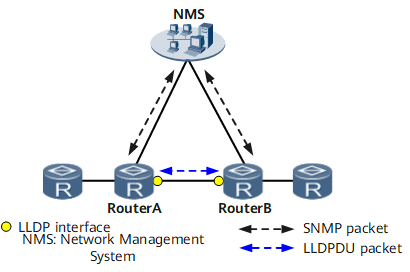
LLDP Implementation
- Device A encapsulates its status information into an LLDP packet and sends the packet to the neighboring device Device B.
- Device B parses the LLDP packet received and saves information about Device A to its LLDP remote system MIB, allowing the NMS to collect topology information.
- Device B encapsulates its status information into an LLDP packet and sends the packet to the neighboring device Device A. Device A parses the LLDP packet received and saves information about Device B to its LLDP remote system MIB, allowing the NMS to collect topology information.
- By exchanging SNMP packets with Device A and Device B, the NMS collects information about Device A and Device B from their LLDP local system MIBs and LLDP remote system MIBs, and analyzes the status information to determine network topology.
Benefits
Deploying LLDP improves NMS capabilities. LLDP supplies the NMS with detailed information about network topology and topology changes, and it detects inappropriate configurations existing on the network. The information provided by LLDP helps administrators monitor network status in real time to keep the network secure and stable.