Configuring a Basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN
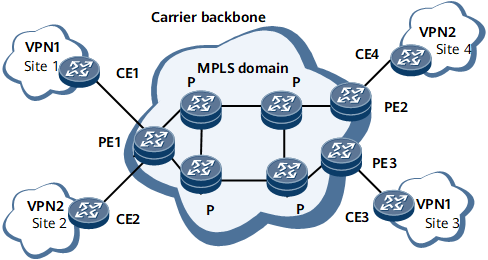
A basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN applies to the scenario in which there is only one carrier or the backbone networks of multiple carriers belong to the same AS, and each device plays only one role, either PE, P, or CE. After a basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN is configured, different sites in a VPN can communicate with each other.
Usage Scenario
After a basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN is configured, the network can provide VPN services for users so that multiple private networks can communicate across the backbone network of the carrier. VPN routes are isolated from the public network routes on the backbone network, and the routes of VPN instances are isolated from each other.
Site1 can communicate with only Site3.
Site2 can communicate with only Site4.
The MPLS backbone network is unaware of the VPN routes in each site.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring a basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN, complete the following tasks:
Configure the routing policy to control the route receiving and sending of the VPN instance IPv4 address family if needed.
Configure an IGP on the PEs and Ps of the MPLS backbone network to ensure IP connectivity on the backbone network.
Establish non-LDP LSP tunnels based on tunnel policies or LDP LSPs on the MPLS backbone network.
Configure IP addresses on interfaces that connect CEs to PEs.
- Configuring a VPN Instance
- A VPN instance can be configured on a PE to manage VPN routes.
- Binding Interfaces to a VPN Instance
- After an interface is bound to a VPN instance, the interface becomes a part of the VPN. Packets entering the interface will be forwarded based on the VRF table of the VPN.
- (Optional) Configuring a Router ID for a BGP-VPN Instance IPv4 Address Family
- You can configure different router IDs for BGP VPN instance IPv4 address families on the same device.
- Establishing MP-IBGP Peer Relationships Between PEs
- MP-IBGP uses extended community attributes to advertise VPNv4 routes between PEs.
- Configuring Route Exchange Between PEs and CEs
- To enable CEs to communicate, the PEs and CEs must be capable of exchanging routes.
- (Optional) Configuring One-Label-per-Next-Hop Label Distribution
- To save label resources on a PE, configure one-label-per-next-hop label distribution on the PE. Only one label is allocated to the VPNv4 routes that have the same next-hop address and outgoing label.
- Verifying the Configuration
- After configuring a basic BGP/MPLS IP VPN, check information about the VPN instance IPv4 address family created on the PE, including the RD and other attributes. You can also check information about IPv4 VPN routes to the local and remote sites on the PE and CE.