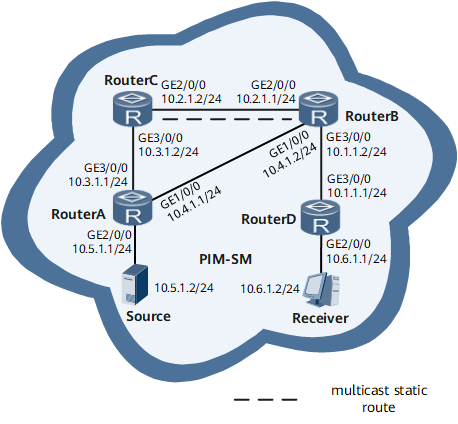
Example for Configuring Multicast Static Routes to Change RPF Routes
To change the Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) route and create a multicast path different from the source-to-receiver unicast path, configure multicast static routes on the multicast network.
Networking Requirements
As shown in Figure 1, the network runs PIM-SM, all routers support multicast, and the receiver can receive information from the multicast source. IS-IS is run between routers. Configure a multicast static route to create a multicast path from the source to the receiver different from the unicast path from the source to the receiver.
Precautions
When configuring multicast static routes to change RPF routes, note the following precautions:
PIM-SM must be enabled before IGMP is enabled.
When configuring a multicast static route, if the next hop is a Point-to-point (P2P) interface, you must specify the outbound interface number; if the next hop is not a P2P interface, you must specify the next-hop address.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each router interface and configure IS-IS on routers.
Enable multicast routing on each router, enable PIM-SM on each interface, and enable IGMP on interfaces connecting routers to hosts.
Configure Candidate-BootStrap Routers (C-BSRs) and Candidate-Rendezvous Points (C-RPs).
Configure multicast static routes on Device B and specify Device C as an RPF neighbor to the source.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP address of the source
Outbound interface of Device B to the source
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each router interface and a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable multicast routing on each router and PIM-SM on each router interface.
# Configure Device A. The configurations of Device B, Device C, and Device D are similar to the configuration of Device A. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceA] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] pim sm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit
- Enable IGMP on interfaces that connect to hosts.
# Enable IGMP on the interface connecting Device D to hosts.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] igmp enable [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
- Configure C-BSRs and C-RPs.
# Configure GE 0/1/16 on Device C as both a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[~DeviceC] pim [*DeviceC] c-bsr GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceC] c-rp GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceC] commit [~DeviceC] quit
# Run the display multicast rpf-info command on Device B to view the RPF information of the source. The command output shows that the RPF route is a unicast route and the RPF neighbor is Device A.
<DeviceB> display multicast rpf-info 10.5.1.2 VPN-Instance: public net RPF information about source 10.5.1.2: RPF interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, RPF neighbor: 10.4.1.1 Referenced route/mask: 10.5.1.0/24 Referenced route type: unicast Route selection rule: preference-preferred Load splitting rule: disable
- Configure multicast static routes.
# Configure a multicast static route on Device B and specify Device C as an RPF neighbor to the source.
<DeviceB> system-view [~DeviceB] ip rpf-route-static 10.5.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.2.1.2 [*DeviceB] commit [~DeviceB] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display multicast rpf-info command on Device B to view the RPF information of the source. The command output shows that the RPF route and the RPF neighbor are updated based on the multicast static route.
<DeviceB> display multicast rpf-info 10.5.1.2 VPN-Instance: public net RPF information about source 10.5.1.2: RPF interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8, RPF neighbor: 10.2.1.2 Referenced route/mask: 10.5.1.0/24 Referenced route type: mstatic Route selection rule: preference-preferred Load splitting rule: disable
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # multicast routing-enable # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.5.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast routing-enable # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # ip rpf-route-static 10.5.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.2.1.2 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast routing-enable # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # pim c-bsr GigabitEthernet0/1/16 c-rp GigabitEthernet0/1/16 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # multicast routing-enable # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.6.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # return