Example for Configuring Basic MLD Functions
This section provides an example for configuring basic MLD functions.
Networking Requirements
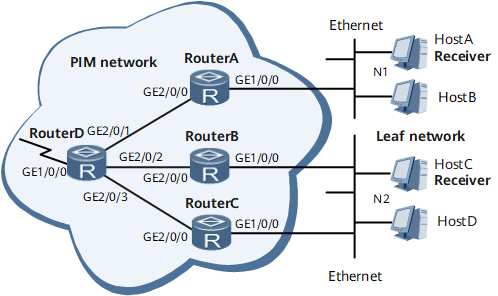
On the ISP network shown in Figure 1, IPv6 multicast services are deployed. An IGP has been deployed to ensure that IPv6 unicast routes are available. Hosts on this network want to receive VOD information with the IPv6 multicast service. For example, Host A and Host B want to join multicast group FF13::101 to steadily receive popular programs.
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
DeviceA |
GigabitEthernet0/1/1 |
2001:db8:1::1/64 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:5::1/64 |
|
DeviceB |
GigabitEthernet0/1/1 |
2001:db8:2::1/64 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:6::1/64 |
|
DeviceC |
GigabitEthernet0/1/1 |
2001:db8:3::1/64 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:7::1/64 |
|
DeviceD |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:4::1/64 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/1 |
2001:db8:1::2/64 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/2 |
2001:db8:2::2/64 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/3 |
2001:db8:3::2/64 |
Precautions
When configuring basic MLD functions, note the following precautions:
IPv6 PIM-SM must be enabled before MLD is enabled.
Interfaces connected to the same user network segment must run the same MLD version.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IPv6 address for each router interface and an IPv6 unicast routing protocol.
Enable IPv6 multicast routing on all routers.
Enable IPv6 PIM-SM on all router interfaces.
Enable MLD on interfaces that connect to hosts.
Configure GE 0/1/0 on DeviceA to statically join MLD group FF13::101 to steadily receive multicast data.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Version numbers of MLD run on routers and user hosts
Address of the MLD group that interface statically joins
Procedure
- Configure an IPv6 address for each router interface and a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable IPv6 multicast routing on each router and enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each router interface.
# Configure DeviceD. The configurations of DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC are similar to the configuration of DeviceD. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceD] multicast ipv6 routing-enable [*DeviceD] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim ipv6 sm [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceD] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim ipv6 sm [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DeviceD] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*DeviceD] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/3 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] pim ipv6 sm [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
- Configure a Rendezvous Point (RP).
# Configure a dynamic RP on DeviceD.
[~DeviceD] pim-ipv6 [*DeviceD-pim6] c-bsr 2001:db8:4::1 [*DeviceD-pim6] c-rp 2001:db8:4::1 [*DeviceD-pim6] commit [~DeviceD-pim6] quit
- Enable MLD on interfaces that connect to hosts.
# Configure DeviceA. The configurations of DeviceB and DeviceC are similar to the configuration of DeviceA. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mld enable [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure GE 0/1/0 on DeviceA to statically join MLD group FF13::101.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mld static-group ff13::101 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display mld interface command to view brief MLD information on the interfaces of the router. For example, MLD information on GE 0/1/0 of DeviceB is as follows:
<DeviceB> display mld interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0(FE80::200:5EFF:FE66:5100): MLD is enabled Current MLD version is 1 MLD state: up MLD group policy: none Value of query interval for MLD (negotiated): 125 s Value of query interval for MLD (configured): 125 s Value of other querier timeout for MLD: 0 s Value of maximum query response time for MLD: 10 s
The command output shows that DeviceB is a querier. This is because GE 0/1/0 of DeviceB has the lowest IPv6 address among the interfaces connected to the user network segment.
# Run the display pim ipv6 routing-table command on DeviceA to check whether GE 0/1/0 has joined MLD group FF13::101 statically. The command output shows that a (*, FF13::101) entry has been generated, the downstream interface is GE 0/1/0, and the protocol type is MLD. The following information is displayed:
<DeviceA> display pim ipv6 routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 0 (S, G) entry (*, FF13::101) RP: 2001:db8:4::1 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:12:17 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1, Refresh time: 00:12:17 Upstream neighbor: 2001:db8:1::1 RPF prime neighbor: 2001:db8:1::1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:12:17, Expires: -
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # isis 1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:5::1/64 pim ipv6 sm mld enable mld static-group ff13::101 isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::1/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # isis 1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:6::1/64 pim ipv6 sm mld enable isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # isis 1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:7::1/64 pim ipv6 sm mld enable isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # return
DeviceD configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # isis 1 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::1/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::2/64 pim ipv6 sm isis ipv6 enable 1 # pim-ipv6 c-bsr 2001:db8:4::1 c-rp 2001:db8:4::1 # return