Example for Configuring BFD for IPv6 PIM
This section provides an example for configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for IPv6 PIM, so that user hosts can quickly respond to Designated router (DR) changes.
Networking Requirements
In multicast applications, if the current DR is faulty on the shared network segment, other PIM neighbors do not trigger a new round of DR election until the neighbor relationships time out. Consequently, multicast data transmission is interrupted. The period during which multicast data transmission is interrupted, usually in seconds, is not shorter than the timeout period of the neighbor relationship. BFD can detect the link status on the shared network segment within milliseconds and fast respond to the faults of PIM neighbors. You can use both BFD for IPv6 PIM and the DR switching delay, shortening the transmission interruption time of multicast data and improving the reliability of multicast data transmission.
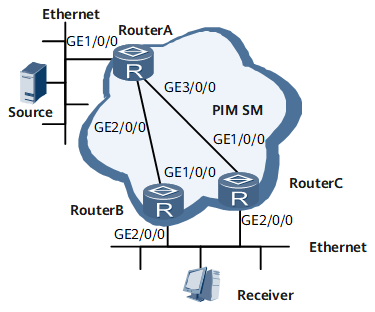
On the network shown in Figure 1, the downstream interface GE 0/1/8 of Device C functions as the current DR and is responsible for forwarding multicast data to Receiver and the host can receive VoD information from the multicast source. After BFD for IPv6 PIM is deployed on the shared network segment where Device B and Device C reside, PIM can quickly detect the fault if the GE 0/1/8 of Device C is faulty. Then, PIM triggers a DR election. The GE 0/1/8 of Device B is immediately elected as the new DR and is responsible for forwarding multicast data. Then, multicast data is immediately switched to the new path. This shortens the period during which multicast data transmission is interrupted and increases the reliability of multicast data transmission. In addition, the DR switchover delay needs to be set. Then, after the faulty DR (the GE 0/1/8 of Device C) on the network recovers, DR election is re-performed and the routing table is rebuilt. During this process, the interface maintains the original multicast forwarding entry to shorten the interruption period of multicast data transmission to the maximum extent.
Device |
Interface |
IPv6 Address |
Link-local address |
|---|---|---|---|
DeviceA |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:1::2/64 |
FE80::2 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
2001:db8:2::1/64 |
FE80::3 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
2001:db8:3::1/64 |
FE80::4 |
|
Loopback0 |
2001:db8:7::7/128 |
FE80::1 |
|
DeviceB |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:2::2/64 |
FE80::5 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
2001:db8:4::1/64 |
FE80::6 |
|
DeviceC |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
2001:db8:3::2/64 |
FE80::8 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
2001:db8:4::2/64 |
FE80::7 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic functions of IPv6 multicast.
Enable BFD globally.
Enable BFD for IPv6 PIM on the interface connecting the router to the network segment to which user hosts belong and configure BFD parameters.
Configure the DR switch delay on the interface connecting the router to the network segment to which user hosts belong.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Multicast source address
Multicast group address
BFD parameters: minimum sending interval, minimum receiving interval, and local detection multiplier of PIM IPv6 BFD packets
DR switchover delay
Procedure
- Configure an IPv6 address and a link-local address for each interface on the router and configure a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Configure an IPv6 address and a link-local address for each interface on the router based on Figure 1 and run OSPFv3 between routers to ensure that they communicate with each other. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable IPv6 multicast routing on all routers. Enable IPv6 PIM-SM on each interface of routers and enable MLD on the interfaces connecting routers to user hosts.
# Configure Device B. The configurations of Device A and Device C are similar to the configuration of Device B. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceB] multicast ipv6 routing-enable [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim ipv6 sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mld enable [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim ipv6 sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure an RP.
# Create a loopback interface on Device A and enable IPv6 PIM-SM; configure the loopback interface to function as both Candidate-Rendezvous Points (C-RPs) and Candidate-BootStrap Routers (C-BSRs).
[~DeviceA] interface loopback 0 [*DeviceA-Loopback0] ipv6 enable [*DeviceA-Loopback0] ipv6 address 2001:db8:7::7 128 [*DeviceA-Loopback0] pim ipv6 sm [*DeviceA-Loopback0] ospfv3 1 area 0 [*DeviceA-Loopback0] quit [*DeviceA] pim-ipv6 [*DeviceA-pim6] c-bsr 2001:db8:7::7 [*DeviceA-pim6] c-rp 2001:db8:7::7 [*DeviceA-pim6] commit [~DeviceA-pim6] quit
- Enable BFD globally, configure BFD for IPv6 PIM on the interfaces connecting the routers to the user network segment, and configure BFD parameters.
# Configure Device B. The configuration of Device C is similar to the configuration of Device B. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceB] bfd [*DeviceB-bfd] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim ipv6 bfd enable [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim ipv6 bfd min-tx-interval 200 min-rx-interval 200 detect-multiplie 4 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
- Configure the DR switch delay on the interfaces that connect routers to the user network segment.
# Configure router B. The configuration of router C is similar to the configuration of router B. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim ipv6 timer dr-switch-delay 20 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceB] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Have the multicast source (2001:db8:1::1) send data to the multicast group (FF2E::1) and have Receiver send an MLD Report message to the multicast group. Ensure that Receiver can receive the data from the multicast source. Run the display pim ipv6 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose command to check detailed configurations of the PIM interface connecting the router to the user host.
<DeviceB> display pim ipv6 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose VPN-Instance: public net Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8, FE80::6 PIM version: 2 PIM mode: Sparse PIM state: up PIM DR: FE80::7 PIM DR Priority (configured): 1 PIM neighbor count: 1 PIM hello interval: 30 s PIM LAN delay (negotiated): 500 ms PIM LAN delay (configured): 500 ms PIM hello override interval (negotiated): 2500 ms PIM hello override interval (configured): 2500 ms PIM Silent: disabled PIM neighbor tracking (negotiated): disabled PIM neighbor tracking (configured): disabled PIM generation ID: 0X1DD32289 PIM require-GenID: disabled PIM hello hold interval: 105 s PIM assert hold interval: 180 s PIM triggered hello delay: 5 s PIM J/P interval: 60 s PIM J/P hold interval: 210 s PIM BSR domain border: disabled PIM BFD: enabled PIM BFD min-tx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD min-rx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD detect-multiplier: 4 PIM dr-switch-delay timer: 20 s Number of routers on link not using DR priority: 0 Number of routers on link not using LAN delay: 0 Number of routers on link not using neighbor tracking: 2 ACL of PIM neighbor policy: - ACL of PIM ASM join policy: - ACL of PIM SSM join policy: - ACL of PIM join policy: - PIM ipsec: enabled (sa-name: 1) <DeviceC> display pim ipv6 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose VPN-Instance: public net Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8, FE80::7 PIM version: 2 PIM mode: Sparse PIM state: up PIM DR: FE80::7 (local) PIM DR Priority (configured): 1 PIM neighbor count: 1 PIM hello interval: 30 s PIM LAN delay (negotiated): 500 ms PIM LAN delay (configured): 500 ms PIM hello override interval (negotiated): 2500 ms PIM hello override interval (configured): 2500 ms PIM Silent: disabled PIM neighbor tracking (negotiated): disabled PIM neighbor tracking (configured): disabled PIM generation ID: 0X8365186A PIM require-GenID: disabled PIM hello hold interval: 105 s PIM assert hold interval: 180 s PIM triggered hello delay: 5 s PIM J/P interval: 60 s PIM J/P hold interval: 210 s PIM BSR domain border: disabled PIM BFD: enabled PIM BFD min-tx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD min-rx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD detect-multiplier: 4 PIM dr-switch-delay timer: 20 s Number of routers on link not using DR priority: 0 Number of routers on link not using LAN delay: 0 Number of routers on link not using neighbor tracking: 2 ACL of PIM neighbor policy: - ACL of PIM ASM join policy: - ACL of PIM SSM join policy: - ACL of PIM join policy: - PIM ipsec: enabled (sa-name: 1)
The preceding information indicates that the downstream interface GE 0/1/8 of Device C is the current DR. BFD for IPv6 PIM is enabled on the interfaces connecting Device B and Device C to user hosts, and detection parameters and a DR switchover delay are configured.
# Run the display pim ipv6 neighbor interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose command on Device B to check whether BFD sessions are set up.
<DeviceB> display pim ipv6 neighbor interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose VPN-Instance: public net Total Number of Neighbors on this interface = 1 Neighbor: FE80::7 Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Uptime: 00:00:52 Expiry time: 00:01:39 DR Priority: 1 Generation ID: 0X8365186A Holdtime: 105 s LAN delay: 500 ms Override interval: 2500 ms Neighbor tracking: Disabled PIM BFD-Session: Y PIM BFD-Session min-tx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD-Session min-rx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD-Session detect-multiplier: 4 Neighbor Secondary Address(es): 2001:db8:4::2
The command output shows that the BFD sessions are set up.
# Run the display pim ipv6 bfd session command to check configurations of BFD sessions on each router.
<DeviceB> display pim ipv6 bfd session VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 BFD session Created GigabitEthernet0/1/8 (FE80::6): Total 1 BFD session Created Neighbor ActTx(ms) ActRx(ms) ActMulti Local/Remote State FE80::7 200 200 4 8208/8206 Up <DeviceC> display pim ipv6 bfd session VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 BFD session Created GigabitEthernet0/1/8 (FE80::7): Total 1 BFD session Created Neighbor ActTx(ms) ActRx(ms) ActMulti Local/Remote State FE80::6 200 200 4 8206/8208 Up
The command output shows that the BFD session is in the Up state, and the sending interval and receiving interval of BFD packets are both 200 ms, and the detection multiplier is 4.
# Run the display pim ipv6 routing-table command to check the IPv6 PIM routing table. The command output on Device C shows that multicast routing entries exist.
<DeviceC> display pim ipv6 routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, FF2E::1) RP: 2001:db8:7::7 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:00:53 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:00:53 Upstream neighbor: FE80::4 RPF prime neighbor: FE80::4 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:00:53, Expires: - (2001:db8:1::1, FF2E::1) RP: 2001:db8:7::7 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT UpTime: 00:00:53 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:00:53 Upstream neighbor: FE80::4 RPF prime neighbor: FE80::4 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:00:53, Expires: -
# Simulate a fault on the downstream GE 0/1/8 of Device C and run the display pim ipv6 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose command on Device B to check detailed information about the PIM interface. The command output is as follows:
<DeviceB> display pim ipv6 interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 verbose VPN-Instance: public net Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8, FE80::6 PIM version: 2 PIM mode: Sparse PIM state: up PIM DR: FE80::6 (local) PIM DR Priority (configured): 1 PIM neighbor count: 1 PIM hello interval: 30 s PIM LAN delay (negotiated): 500 ms PIM LAN delay (configured): 500 ms PIM hello override interval (negotiated): 2500 ms PIM hello override interval (configured): 2500 ms PIM Silent: disabled PIM neighbor tracking (negotiated): disabled PIM neighbor tracking (configured): disabled PIM generation ID: 0X1DD32289 PIM require-GenID: disabled PIM hello hold interval: 105 s PIM assert hold interval: 180 s PIM triggered hello delay: 5 s PIM J/P interval: 60 s PIM J/P hold interval: 210 s PIM BSR domain border: disabled PIM BFD: enabled PIM BFD min-tx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD min-rx-interval: 200 ms PIM BFD detect-multiplier: 4 PIM dr-switch-delay timer: 20 s Number of routers on link not using DR priority: 0 Number of routers on link not using LAN delay: 0 Number of routers on link not using neighbor tracking: 2 ACL of PIM neighbor policy: - ACL of PIM ASM join policy: - ACL of PIM SSM join policy: - ACL of PIM join policy: - PIM ipsec: enabled (sa-name: 1)
The command output shows that after GE 0/1/8 of Device C fails, GE 0/1/8 of Device B is elected as the DR.
# Run the display pim ipv6 routing-table command to check the IPv6 PIM routing table. The command output on Device B shows that multicast routing entries exist.
<DeviceB> display pim ipv6 routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, FF2E::1) RP: 2001:db8:7::7 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:00:53 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:00:53 Upstream neighbor: FE80::3 RPF prime neighbor: FE80::3 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: mld, UpTime: 00:00:53, Expires: - (2001:db8:1::1, FF2E::1) RP: 2001:db8:7::7 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT UpTime: 00:00:53 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:00:53 Upstream neighbor: FE80::3 RPF prime neighbor: FE80::3 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:00:53, Expires: -
The command output shows that after GE 0/1/8 of Device C fails, multicast traffic is fast switched to a new path. GE 0/1/8 of Device B is elected as a new DR.
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # ipv6 # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # ospfv3 1 router-id 10.2.2.2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:1::2/64 ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::1/64 ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::1/64 ipv6 address FE80::4 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 sm # interface LoopBack0 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:7::7/128 ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 sm # pim-ipv6 c-bsr 2001:db8:7::7 c-rp 2001:db8:7::7 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # ipv6 # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # bfd # ospfv3 1 router-id 10.3.3.3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:2::2/64 ipv6 address FE80::5 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::1/64 ipv6 address FE80::6 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 timer dr-switch-delay 20 pim ipv6 sm pim ipv6 bfd enable pim ipv6 bfd min-tx-interval 200 min-rx-interval 200 detect-multiplier 4 mld enable # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # ipv6 # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # bfd # ospfv3 1 router-id 10.4.4.4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:3::2/64 ipv6 address FE80::8 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:db8:4::2/64 ipv6 address FE80::7 link-local ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 pim ipv6 timer dr-switch-delay 20 pim ipv6 sm pim ipv6 bfd enable pim ipv6 bfd min-tx-interval 200 min-rx-interval 200 detect-multiplier 4 mld enable # return