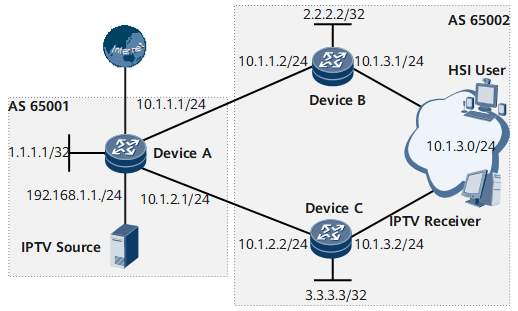
Example for Separating Unicast Traffic from Multicast Traffic
Separating unicast traffic from multicast traffic helps plan the MBGP network.
Networking Requirements
In Figure 1, Device A resides in AS 65001 and is connected to the Internet and an IPTV multicast source; Device B and Device C reside in AS 65002 and are connected to high-speed Internet (HSI) users and IPTV users. It is required that the unicast traffic from AS 65001 to AS 65002 be separated from the multicast traffic from AS 65001 to AS 65002. Specifically, the HSI traffic is forwarded by Device B, whereas the IPTV traffic is forwarded by Device C.
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
DeviceA |
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.2.1/24 |
|
GE0/1/8 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
GE0/1/16 |
192.168.1.1/24 |
|
DeviceB |
Loopback1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
GE0/1/8 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
GE0/1/16 |
10.1.3.1/24 |
|
DeviceC |
Loopback1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
GE0/1/0 |
10.1.2.2/24 |
|
GE0/1/16 |
10.1.3.2/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each interface and unicast routes so that devices within an AS can communicate with each other.
Establish Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) peer relationships to generate inter-AS multicast routes.
Configure the routes to be advertised and configure route-policies to control the routes to be advertised by Device B and Device C to Device A so that Device A can separate unicast BGP routes from MBGP routes.
Enable the multicast function on each device.
Configure the bootstrap router (BSR) boundary on inter-AS connected interfaces.
Establish MSDP peer relationships to transmit inter-AS multicast source information.
Verify the configuration.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- AS 65001 for Device A and AS 65002 for Device B and Device C
- Route-policy named policy_b2a on Device B, used to change the MED of the MBGP route to be advertised to Device A to 120
- Route-policy named policy_c2a on Device C, used to change the MED of the unicast BGP route to be advertised to Device A to 160
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface and enable OSPF within AS 65002.
# Configure an IP address and a mask for each interface and enable a unicast routing protocol within AS 65002 to update routes dynamically. For configuration details, see Figure 1. In this example, OSPF is used as the unicast routing protocol, with process ID 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure BGP, enable MBGP, and establish MBGP peer relationships.
# Configure BGP and establish MBGP peer relationships on Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 65001 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65002 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.1.2.2 as-number 65002 [*DeviceA-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [*DeviceA-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.1.2 enable [*DeviceA-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.2.2 enable [*DeviceA-bgp-af-multicast] commit [~DeviceA-bgp-af-multicast] quit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
# Configure BGP and establish MBGP peer relationships on Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 65002 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65001 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.1.3.2 as-number 65002 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.1.1 enable [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.3.2 enable [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] quit
# Configure BGP and establish MBGP peer relationships on Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 65002 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.1.2.1 as-number 65001 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.1.3.1 as-number 65002 [*DeviceC-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [*DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.2.1 enable [*DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.3.1 enable [*DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] commit [~DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] quit
- Configure the routes to be advertised.
# Configure the routes to be advertised on Device B.
[~DeviceB-bgp] network 2.2.2.2 32 [*DeviceB-bgp] network 10.1.3.0 24 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] network 2.2.2.2 32 [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] network 10.1.3.0 24 [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure the routes to be advertised on Device C.
[~DeviceC-bgp] network 3.3.3.3 32 [*DeviceC-bgp] network 10.1.3.0 24 [*DeviceC-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [*DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] network 3.3.3.3 32 [*DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] network 10.1.3.0 24 [*DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] commit [~DeviceC-bgp-af-multicast] quit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
- Configure route-policies.
# Configure a route-policy on Device B to change the MED of the MBGP route to be advertised to Device A so that Device A selects the MBGP route advertised by Device C.
[~DeviceB] ip ip-prefix p_b2a permit 10.1.3.0 24 [*DeviceB] route-policy policy_b2a permit node 10 [*DeviceB-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix p_b2a [*DeviceB-route-policy] apply cost 120 [*DeviceB-route-policy] quit [*DeviceB] route-policy policy_b2a permit node 20 [*DeviceB-route-policy] quit [*DeviceB] bgp 65002 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv4-family multicast [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] peer 10.1.1.1 route-policy policy_b2a export [*DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-multicast] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure a route-policy on Device C to change the MED of the unicast BGP route to be advertised to Device A so that Device A selects the unicast BGP route advertised by Device B.
[~DeviceC] ip ip-prefix p_c2a permit 10.1.3.0 24 [*DeviceC] route-policy policy_c2a permit node 10 [*DeviceC-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix p_c2a [*DeviceC-route-policy] apply cost 160 [*DeviceC-route-policy] quit [*DeviceC] route-policy policy_c2a permit node 20 [*DeviceC-route-policy] quit [*DeviceC] bgp 65002 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 10.1.2.1 route-policy policy_c2a export [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
Check the unicast BGP routing table and MBGP routing table on Device A.
[~DeviceA] display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Total Number of Routes: 5 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 1.1.1.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 i *> 2.2.2.2/32 10.1.1.2 0 0 65002i *> 3.3.3.3/32 10.1.2.2 0 0 65002i *> 10.1.3.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 0 65002i * 10.1.2.2 160 0 65002i
The preceding command output shows that Device A selects the unicast BGP route advertised by Device B as the optimal unicast route to transmit the traffic destined for 10.1.3.0/24.
[~DeviceA] display bgp multicast routing-table BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Total Number of Routes: 5 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 1.1.1.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 i *> 2.2.2.2/32 10.1.1.2 0 0 65002i *> 3.3.3.3/32 10.1.2.2 0 0 65002i *> 10.1.3.0/24 10.1.2.2 0 0 65002i * 10.1.1.2 120 0 65002i
The preceding command output shows that Device A selects the MBGP route advertised by Device C as the optimal multicast route to transmit the traffic destined for 10.1.3.0/24.
- Enable the multicast function on the devices and interconnected interfaces of the devices.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceA] interface loopback 1 [*DeviceA-LoopBack1] pim sm [*DeviceA-LoopBack1] commit [~DeviceA-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] pim sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] igmp enable [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceB] interface loopback 1 [*DeviceB-LoopBack1] pim sm [*DeviceB-LoopBack1] commit [~DeviceB-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] pim sm [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] igmp enable [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceC] interface loopback 1 [*DeviceC-LoopBack1] pim sm [*DeviceC-LoopBack1] commit [~DeviceC-LoopBack1] quit
- Configure the C-BSR and candidate-rendezvous point (C-RP) to run for the BSR and RP.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] pim [*DeviceA-pim] c-bsr loopback 1 [*DeviceA-pim] c-rp loopback 1 [*DeviceA-pim] commit [~DeviceA-pim] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] pim [*DeviceC-pim] c-bsr loopback 1 [*DeviceC-pim] c-rp loopback 1 [*DeviceC-pim] commit [~DeviceC] quit
- Configure the BSR boundary on inter-AS connected interfaces.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Establish MSDP peer relationships.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] msdp [*DeviceA-msdp] peer 10.1.1.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*DeviceA-msdp] peer 10.1.2.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceA-msdp] commit [~DeviceA-msdp] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] msdp [*DeviceB-msdp] peer 10.1.1.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*DeviceB-msdp] commit [~DeviceB-msdp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] msdp [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 10.1.2.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceC-msdp] commit [~DeviceC-msdp] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display msdp brief command to check whether MSDP peer relationships are established. The command output on Device A is used as an example.
[~DeviceA] display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 2 2 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 10.1.1.2 Up 01:04:26 65002 0 0 10.1.2.2 Up 01:04:13 65002 0 0
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 shutdown pim sm # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 pim sm # bgp 65001 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 65002 peer 10.1.2.2 as-number 65002 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.2 enable peer 10.1.2.2 enable # ipv4-family multicast undo synchronization network 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.2 enable peer 10.1.2.2 enable # pim c-bsr LoopBack1 c-rp LoopBack1 # msdp peer 10.1.1.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 peer 10.1.2.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 pim sm # bgp 65002 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65001 peer 10.1.3.2 as-number 65002 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 network 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.1.1.1 enable peer 10.1.3.2 enable # ipv4-family multicast undo synchronization network 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 network 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.1.1.1 enable peer 10.1.1.1 route-policy policy_b2a export peer 10.1.3.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy_b2a permit node 10 if-match ip-prefix p_b2a apply cost 120 # route-policy policy_b2a permit node 20 # msdp peer 10.1.1.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 # ip ip-prefix p_b2a index 10 permit 10.1.3.0 24 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 pim sm # bgp 65002 peer 10.1.2.1 as-number 65001 peer 10.1.3.1 as-number 65001 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 network 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.1.2.1 enable peer 10.1.2.1 route-policy policy_c2a export peer 10.1.3.1 enable # ipv4-family multicast undo synchronization network 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 network 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 peer 10.1.2.1 enable peer 10.1.3.1 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy_c2a permit node 10 if-match ip-prefix p_c2a apply cost 160 # route-policy policy_c2a permit node 20 # pim c-bsr LoopBack1 c-rp LoopBack1 # msdp peer 10.1.2.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 # ip ip-prefix p_c2a index 10 permit 10.1.3.0 24 # return