Example for Configuring PIM FRR
This section provides an example for configuring PIM FRR. PIM FRR helps minimize multicast traffic loss caused by link or node failures on networks that have high real-time transmission requirements.
Networking Requirements
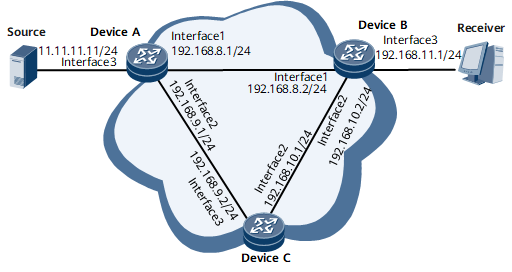
On the network shown in Figure 1, configure PIM FRR to enable multicast traffic to be switched to a backup link when the primary link or node fails.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign IP addresses to router interfaces and configure a unicast routing protocol.
Configure IS-IS FRR on routerB.

Unicast route FRR can be configured for either static or dynamic routes, or for both of them. This example uses IS-IS FRR.
Enable multicast routing and PIM-SM on all routers that provide the multicast service.
Configure a static IGMP group on the router interface connected to hosts.
Configure a rendezvous point (RP).
Enable PIM FRR on routerB.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Multicast group address: 225.1.0.0
Multicast source address: 10.0.5.100
Procedure
- Assign IP addresses to interfaces and configure a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure IS-IS FRR on routerB.
[~Device B] isis 1 [*Device B-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 [*Device B-isis-1] frr [*Device B-isis-1-frr] loop-free-alternate level-1 [*Device B-isis-1-frr] commit
- Enable multicast routing on each router and PIM-SM on each interface.
# Enable multicast routing on each router and PIM-SM on each interface of the routers.
[~Device B] multicast routing-enable [*Device B] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*Device B-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*Device B-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*Device B] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*Device B-Gigabitethernet0/1/2] pim sm [*Device B-Gigabitethernet0/1/2] quit [*Device B] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [*Device B-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] pim sm [*Device B-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*Device B] commit
The configurations of DeviceA and DeviceC are similar to the configuration of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure a static IGMP group on the Device interface connected to hosts to simulate a user join.
# Configure a static IGMP group on DeviceB's interface connected to hosts.
[~Device B] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [~Device B-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] igmp static-group 225.1.0.0 source 10.0.5.100 [*Device B-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*Device B] commit
- Configure an RP.
# Configure a candidate-BSR (C-BSR) and candidate-RP (C-RP) on DeviceB.
[~Device B] pim [~Device B-pim] c-bsr gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*Device B-pim] c-rp gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*Device B-pim] quit [*Device B] commit
# Check the PIM routing table of DeviceB. The command output does not show backup inbound or outbound interface information.
[~Device B] display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.0.5.100, 225.1.0.0) RP: 192.168.8.2 (local) Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT SG_RCVR UpTime: 01:21:36 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1, Refresh time: 01:21:36 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.8.1 RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.8.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/3 Protocol: static, UpTime: 01:05:00, Expires: -
- Enable PIM FRR on DeviceB.
[~Device B] acl name frracl [*Device B-acl4-advance-frracl] rule permit ip source 10.0.5.100 0 destination 225.1.0.0 0 [*Device B-acl4-advance-frracl] commit [~Device B-acl4-advance-frracl] quit [~Device B] pim [~Device B-pim] rpf-frr policy acl-name frracl [*Device B-pim] quit [*Device B] commit
The configurations of DeviceA and DeviceC are similar to the configuration of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
# Check the PIM routing table of DeviceB. The command output shows backup inbound interface information.
[*Device B] display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.0.5.100, 225.1.0.0) RP: 192.168.8.2 (local) Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT SG_RCVR UpTime: 01:22:40 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1, Refresh time: 01:22:40 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.8.1 RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.8.1 Backup upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Backup upstream neighbor: 192.168.10.1 Backup RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.10.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/3 Protocol: static, UpTime: 01:06:04, Expires: -
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the shutdown command on GE 0/1/1 of DeviceA to simulate a link failure.
[~Device A] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*Device A-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] shutdown [*Device A-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit
# Run the display pim routing-table command on DeviceB immediately after the shutdown command is run.
[~Device B] display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.0.5.100, 225.1.0.0) RP: NULL Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT SG_RCVR UpTime: 01:24:22 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2, Refresh time: 01:24:22 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.10.1 RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.10.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/3 Protocol: static, UpTime: 01:07:46, Expires: -
The command output shows that the inbound interface of the forwarding route on DeviceB has been switched to GE 0/1/2 on the backup link.
Configuration Files
DeviceA configuration file
# sysname Device A # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.5.100 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.8.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.9.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # return
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname Device B # acl name frracl rule permit ip source 10.0.5.100 0 destination 225.1.0.0 0 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 frr loop-free-alternate level-1 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.8.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 igmp static-group 225.1.0.0 source 10.0.5.100 # pim rpf-frr policy acl-name frracl # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname Device C # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.9.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # return