Example for Establishing Communication Between the NMS and a Device Using NETCONF
This section provides an example for logging in to the server from the client using the NMS to perform remote configuration management.
Networking Requirements
NETCONF ensures security and extensibility. When the NMS is used to manage network devices, you can use NETCONF to ensure communication between the NMS and the devices.
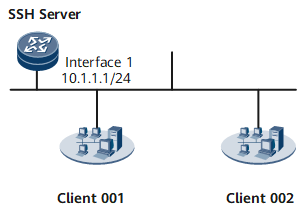
As shown in Figure 1, the NMS is deployed on the client that functions as the SSH client. The server functions as the SSH server that receives connection requests from and establishes the connection with the SSH client. SSH is a security protocol at the application layer, enhancing the reliability of NETCONF. In this networking, NETCONF is used to manage the configuration of the SSH server.

Interface 1 in this example represents GigabitEthernet0/0/0.
Precautions
An SSH user named client001 is used as an example. If the password authentication mode is used to authentication the SSH user, the server needs to generate an Elliptic Curves Cryptography (ECC) key.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure an IP address for the server port connecting to the NMS so that the Layer 3 route between the client and server is reachable.
Configure virtual type terminal (VTY) user interfaces on the server to support SSH so that SSH users can be managed and monitored with better connection security.
Deploy SSH on the server to improve NETCONF security.
- Create an SSH user with administrator rights.
- Create an ECC key pair.
- Configure an authentication mode for the SSH user.
- Configure a service type for the SSH user.
- Enable NETCONF so that the client can connect to the server.
- Deploy the NMS on the client to implement NMS-based network management on the client.
Log in to the server using the NMS to manage the configuration remotely.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
SSH username and authentication mode
SSH user password
SSH server name
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for the server port connecting to the NMS.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname netconf-agent [*HUAWEI] commit [~netconf-agent] interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 [~netconf-agent-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [*netconf-agent-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] commit [~netconf-agent-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] quit
- Configure VTY user interfaces on the server to support SSH.
[~netconf-agent] user-interface vty 0 4 [*netconf-agent-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode aaa [*netconf-agent-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh [*netconf-agent-ui-vty0-4] commit [~netconf-agent-ui-vty0-4] quit

After SSH is configured, the NetEngine 8000 F automatically disables the Telnet function.
- Deploy SSH on the server.
Create an SSH user.
# Create an SSH user with the name client001 and set the user password to Hello-huawei123.
[*netconf-agent] aaa [*netconf-agent-aaa] local-user client001 password cipher Hello-huawei123 [*netconf-agent-aaa] local-user client001 user-group manage-ug [*netconf-agent-aaa] local-user client001 service-type ssh [*netconf-agent-aaa] commit [~netconf-agent-aaa] quit
Create ECC key pair.
[~netconf-agent] ecc local-key-pair create The key name will be: HUAWEI_Host_ECC % ECC keys defined for HUAWEI_Host_ECC already exist. Confirm to replace them? Please select [Y/N]: Y The public key size should be (256/384/521). NOTE: If the key modulus is greater than 256, it will take a few minutes. Input the bits(256/384/521) in the modulus [default = 521] : 256 [*netconf-agent] commit
After the ECC key pair is created, run the display ecc local-key-pair public command to view information about the public key in the ECC key pair.
Configure an authentication mode for the SSH user.
[~netconf-agent] ssh user client001 authentication-type password [*netconf-agent] commit
Configure a service type for the SSH user.
[~netconf-agent] ssh user client001 service-type all [*netconf-agent] commit
- Enable NETCONF on the server.
[~netconf-agent] snetconf server enable [*netconf-agent] commit
- Deploy the NMS on the client.
For installation and maintenance of the NMS, see the relevant installation instruction and usage guidelines.

If the Huawei NMS is used, creating NEs will consume specific upgrade licenses or NE resource licenses. If there are no remaining NE resources or specific upgrade licenses, the system displays a message indicating that an NE fails to be created. If this occurs, apply for NE resources or specific upgrade licenses.
- Log in to the server from the client using the NMS.
For login to remote devices using the NMS, see the relevant usage guide of the NMS.
If a Huawei NMS is used, contact Huawei technical personnel for the NMS operation manual.
- Verify the configuration.
After the preceding configuration is complete, you can log in to the remote device using NETCONF to manage its configuration remotely.

All the following operations are performed on the SSH server.
# Run the display users command to view information about users who have logged in to the server.
[~netconf-agent] display users User-Intf Delay Type Network Address AuthenStatus AuthorcmdFlag 100 NCA 0 00:02:50 SSH 10.2.2.2 pass yes Username : client001# Run the display ssh user-information command to view SSH user information.
[~netconf-agent] display ssh user-information -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- User Name : client001 Authentication-Type : password User-public-key-name : - User-public-key-type : - Sftp-directory : - Service-type : snetconf -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 1, 1 printed# Run the display local-user user-group manage-ug command to view information about local users in user group.
[~netconf-agent] display local-user user-group manage-ug --------------------------------------------------------------------- Username State Type Access-limit Online --------------------------------------------------------------------- client001 Active S No 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 1, 1 printed# Run the display ssh server status command to view global configuration of the SSH server.
[~netconf-agent] display ssh server status SSH Version : 1.99 SSH authentication timeout (Seconds) : 60 SSH authentication retries (Times) : 3 SSH server key generating interval (Hours) : 0 SSH version 1.x compatibility : Enable SSH server keepalive : Disable SFTP server : Disable STELNET server : Disable SNETCONF server : Enable SNETCONF server port(830) : Disable SSH server port : 22 ACL name : ACL number : ACL6 name : ACL6 number : SSH server source address : 0.0.0.0# Run the display netconf capability command to view the capabilities that the server supports.
[~netconf-agent] display netconf capability -------------------------------------------------- Capability -------------------------------------------------- urn:ietf:params:netconf:base:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:base:1.1 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:writable-running:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:candidate:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:confirmed-commit:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:confirmed-commit:1.1 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:rollback-on-error:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:validate:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:validate:1.1 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:startup:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:url:1.0?scheme=file,ftp,sftp urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:xpath:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:notification:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:interleave:1.0 urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:with-defaults:1.0?basic-mode=report-all&also-supported=report-all-tagged,trim urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:yang-library:1.0?revision=2016-06-21&module-set-id=1903662584 --------------------------------------------------
Configuration Files
# sysname netconf-agent # aaa local-user client001 password cipher @%@%U|,(X4rFC)8izE%,QHz:$(|s@%@% local-user client001 service-type ssh local-user client001 user-group manage-ug # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # snetconf server enable ssh user client001 ssh user client001 authentication-type password ssh user client001 service-type all # return