Overview of NG MVPN
Definition
The NG MVPN is a new framework designed to transmit IP multicast traffic across a BGP/MPLS IP VPN. An NG MVPN uses BGP to transmit multicast protocol packets, and uses PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, P2MP TE, or mLDP to transmit multicast data packets. The NG MVPN enables unicast and multicast services to be delivered using the same VPN architecture.
NG MVPN uses BGP to transmit VPN multicast routes and uses MPLS P2MP tunnels to carry VPN multicast traffic so that the traffic can be transmitted from the multicast sources to the remote VPN site over the public network.
Role |
Description |
Corresponding Device |
|---|---|---|
Customer edge (CE) |
A CE directly connects to a service provider network. Usually, a CE is unaware of the VPN and does not need to support MPLS. |
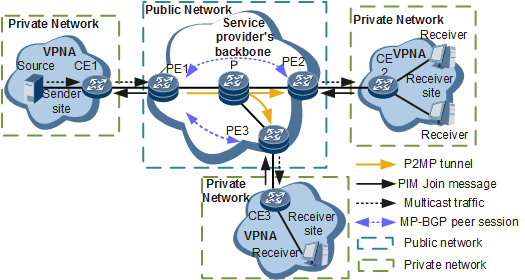
CE1, CE2, and CE3 in Figure 1 |
Provider edge (PE) |
A PE directly connects to CEs. On an MPLS network, PEs process all VPN services. Therefore, the requirements for PE performance are high. |
PE1, PE2, and PE3 in Figure 1 |
Provider device (P) |
A P does not directly connect to CEs. Ps only need to possess basic MPLS forwarding and do not need to maintain VPN information. |
P in Figure 1 |
Receiver Site |
A receiver site is a site where multicast receivers reside. |
Networks where the receivers in Figure 1 reside. |
Receiver PE |
A receiver PE is a PE that connects to a receiver site. |
PE2 and PE3 in Figure 1 |
Sender Site |
A sender site is a site where the multicast source resides. |
Network where the source in Figure 1 resides |
Sender PE |
A sender PE is a PE that connects to a sender site. |
PE1 in Figure 1 |
Purpose
BGP/MPLS IP VPNs are widely deployed as they provide excellent reliability and security. In addition, IP multicast is gaining increasing popularity among service providers as it provides highly efficient point-to-multipoint (P2MP) traffic transmission. Rapidly developing multicast applications, such as IPTV, video conference, and distance education, impose increasing requirements on network reliability, security, and efficiency. As a result, service providers' demand for delivering multicast services over BGP/MPLS IP VPNs is also increasing. In this context, the MVPN solution is developed. The MVPN technology, when applied to a BGP/MPLS IP VPN, can transmit VPN multicast traffic to remote VPN sites across the public network.
Rosen MVPNs establish multicast distribution trees (MDTs) using PIM to transmit VPN multicast protocol and data packets, and have the following limitations:
VPN multicast protocol and data packets must be transmitted using the MDT, which complicates network deployment because the multicast function must be enabled on the public network.
The public network uses GRE for multicast packet encapsulation and cannot leverage the MPLS advantages, such as high reliability, QoS guarantee, and TE bandwidth reservation, of existing BGP/MPLS IP VPNs.
The public network uses BGP to transmit VPN multicast protocol packets and routing information. Multicast protocols do not need to be deployed on the public network, simplifying network deployment and maintenance.
The public network uses the mature label-based forwarding and tunnel protection techniques of MPLS, improving multicast service quality and reliability.
Benefits
NG MVPNs, which implement hierarchical forwarding of multicast data and control packets on BGP/MPLS IP VPNs, offer the following benefits:
Better security by transmitting VPN multicast data over BGP/MPLS IP VPNs.
Better network maintainability by reducing network deployment complexity.
Better service quality and reliability by using mature label-based forwarding and tunnel protection techniques of MPLS.