Example for Collecting IPv4 Flexible Flow Statistics
This section provides an example for collecting IPv4 flexible flow statistics. NetStream enabled on a network can collect network flow statistics.
Networking Requirements
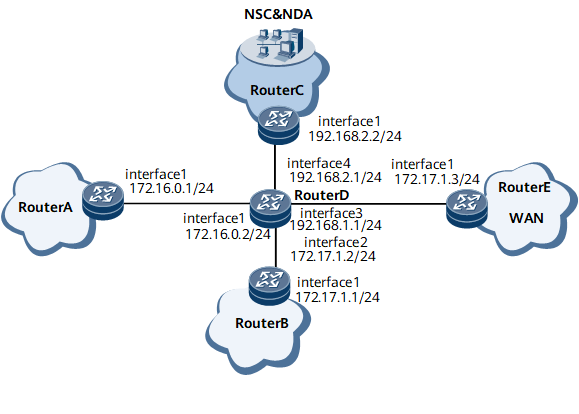
On the network shown in Figure 1, Device D connects network A and network B to the wide area network (WAN). Device D samples and aggregates flows before sending them to the NetStream Collector (NSC).
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure reachable routes between Device A and Device B of the LAN and the WAN.
Configure reachable routes between Device D and the NSC.
Configure Device D to send traffic statistics to the inbound interface on specified NSC.
Configure the flexible flow output function for traffic.
Enable NetStream on the outbound interface of Device D.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP address of each interface
Output format of NetStream flows
NetStream sampling ratio
ID of the slot where the NetStream service processing board resides (In this example, the NetStream service processing board is in slot 1.)
Procedure
- Configure IP addresses for each router. (The configuration details are not provided here.)
- Configure reachable routes between the WAN, Device A, and Device B.
# Configure reachable routes between Device A and Device D.
[~DeviceA] ip route-static 192.168.1.1 24 gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure reachable routes between Device B and Device D.
[~DeviceB] ip route-static 192.168.1.1 24 gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB] commit
# Configure reachable routes between Device D and Device E.
[~DeviceD] ip route-static 172.17.1.3 24 gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceD] commit
- Configure reachable routes between Device D and the NSC.
# Configure reachable routes between Device D and Device C.
[~DeviceD] ip route-static 192.168.2.1 24 192.168.2.2 [*DeviceD] commit
- Enable NetStream on Device D.
# Specify the distributed NetStream sampling mode on a board.
[~DeviceD] slot 1 [~DeviceD-slot-1] ip netstream sampler to slot self [*DeviceD-slot-1] quit [*DeviceD] commit
# Enable the NetStream statistics function for inbound traffic.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip netstream inbound [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceD] commit

NetStream enabled on a main interface cannot collect traffic statistics about its sub-interface.
# Configure the flexible flow template in V9 format.
[~DeviceD] ip netstream record aa [*DeviceD-record-aa] match source as [*DeviceD-record-aa] collect first switched [*DeviceD] commit
# Output flexible flows in V9 format.
[~DeviceD] ip netstream export version 9 [~DeviceD] ip netstream apply record aa [~DeviceD] ip netstream export source 192.168.2.1 [~DeviceD] ip netstream export host 192.168.2.2 3000 [*DeviceD] commit
# Enable the NetStream packet sampling function.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip netstream sampler fix-packets 1000 inbound [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceD] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Check whether the flexible flow template is output correctly.
[~DeviceD] display ip netstream export template ------------------------------------------------------ TemplateName Success Failed ------------------------------------------------------ origin 69 0 Record(system) 14 0
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.0 # ip route-static 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ip route-static 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 # return
- Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # return
Device D configuration file
# slot 1 ip netstream sampler to slot self # sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 172.16.0.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 ip address 172.17.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip route-static 172.17.1.3 24 gigabitethernet 0/1/16 ip netstream inbound ip netstream sampler fix-packets 1000 inbound # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/24 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # ip netstream export version 9 ip netstream export source 192.168.2.1 ip netstream export host 192.168.2.2 3000 # ip netstream record aa match source address collect first switched # ip netstream apply record aa # return
- Device E configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 172.17.1.3 255.255.255.0 # return