Example for Configuring NTP Authentication in Client/Server Mode
You must enable NTP authentication for the NTP client, and then specify the IP address for the NTP server and the authentication key sent to the NTP server. Otherwise, if NTP authentication fails, then no synchronization will take place. In general, for successful NTP authentication, you must completely configure the NTP client and server.
Networking Requirements
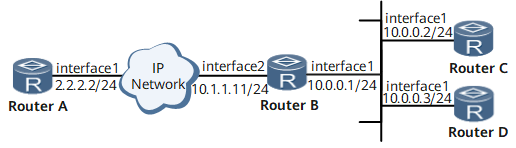
As shown in Figure 1:
Device A functions as a unicast NTP server. The server clock functions as an NTP master clock with the stratum 2.
Device B functions as a unicast NTP client. The client synchronizes clock with Device A.
Device C and Device D function as NTP clients of Device B.
To implement NTP authentication, enable NTP authentication on all routers.

Interfaces 1 and Interface 2 in this example are GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/8 respectively.
Precautions
- Enable NTP authentication on the client before specifying the NTP server address and authentication key to be sent to the server. Otherwise, clock synchronization is implemented without NTP authentication.
- Configure the same authentication key on the NTP server and NTP client and declare the authentication key on the client as reliable. Otherwise, the NTP authentication fails.
- Configure both the server and the client to implement authentication successfully.
- Enable NTP authentication on all the routers.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure the clock on Device A to be the NTP master clock.
Configure Device B to synchronize its clock with the clock of Device A.
Configure Device C and Device D to synchronize their clocks with the clock of Device B.
Enable NTP authentication on all the routers.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP address of the reference clock
Stratum of the NTP master clock
Authentication key and its ID
Procedure
- Configure available routes among the devices. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure the IP addresses based on Figure 1 so that Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D are routable. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an NTP master clock and listening interface on DeviceA and enable NTP authentication.
# On Device A, set its local clock as an NTP master clock with stratum 2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceA [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceA] undo ntp-service server disable [~DeviceA] ntp-service refclock-master 2
# Specify a listening interface on DeviceA.
[~DeviceA] ntp-service server source-interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0
# Enable NTP authentication, and configure the authentication key.
[*DeviceA] ntp-service authentication enable [*DeviceA] ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 Hello123 [*DeviceA] commit

Authentication keys configured on the server and the client must be the same.
- Configure an NTP master clock and listening interface on DeviceB and enable NTP authentication.
# On Device B, enable NTP authentication. Configure the authentication key and declare the key to be reliable.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceB [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceB] undo ntp-service server disable [~DeviceB] ntp-service authentication enable [*DeviceB] ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 Hello123 [*DeviceB] ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42
# Specify a listening interface on DeviceB.
[*DeviceB] ntp-service server source-interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0
# Specify Device A to be the NTP server of Device B and use the authentication key.
[*DeviceB] ntp-service unicast-server 2.2.2.2 authentication-keyid 42 [*DeviceB] commit
- Configure an NTP master clock on Device C and enable NTP authentication.
On Device C, specify Device B to be the NTP server of Device C.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceC [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceC] undo ntp-service server disable [~DeviceC] ntp-service authentication enable [*DeviceC] ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 Hello123 [*DeviceC] ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 [*DeviceC] ntp-service unicast-server 10.0.0.1 authentication-keyid 42 [*DeviceC] commit
- Configure an NTP master clock on Device D and enable NTP authentication.
On Device D, specify Device B to be the NTP server of Device D.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceD [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceD] undo ntp-service server disable [~DeviceD] ntp-service authentication enable [*DeviceD] ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 Hello123 [*DeviceD] ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 [*DeviceD] ntp-service unicast-server 10.0.0.1 authentication-keyid 42 [*DeviceD] commit
- Verify the configuration.
After the configurations are complete, the clock on Device B can be synchronized with the clock on Device A.
Display the NTP status on Device B and find the clock is synchronized. The stratum of the clock is 3, one stratum lower than that on Device A.
[~DeviceB] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 3 reference clock ID: 2.2.2.2 nominal frequency: 60.0002 Hz actual frequency: 60.0002 Hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: 3.8128 ms root delay: 31.26 ms root dispersion: 74.20 ms peer dispersion: 34.30 ms reference time: 11:55:56.833 UTC Mar 2 2006(C7B15BCC.D5604189) synchronization state: clock synchronized
After the configurations are complete, the clock on Device C can be synchronized with the clock on Device B.
Display the NTP status on Device C and find that the clock is synchronized. The stratum of the clock is 4, one stratum lower than that on Device B.
[~DeviceC] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 4 reference clock ID: 10.0.0.1 nominal frequency: 60.0002 Hz actual frequency: 60.0002 Hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: 3.8128 ms root delay: 31.26 ms root dispersion: 74.20 ms peer dispersion: 34.30 ms reference time: 11:55:56.833 UTC Mar 2 2006(C7B15BCC.D5604189) synchronization state: clock synchronized
Display the NTP status on Device D and find that the clock is synchronized. The stratum of the clock is 4, one stratum lower than that on Device B.
[~DeviceD] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 4 reference clock ID: 10.0.0.1 nominal frequency: 60.0002 Hz actual frequency: 60.0002 Hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: 3.8128 ms root delay: 31.26 ms root dispersion: 74.20 ms peer dispersion: 34.30 ms reference time: 11:55:56.833 UTC Mar 2 2006(C7B15BCC.D5604189) synchronization state: clock synchronized
Display NTP status on Device A.
[~DeviceA] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 2 reference clock ID: LOCAL(0) nominal frequency: 60.0002 Hz actual frequency: 60.0002 Hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: 0.0000 ms root delay: 0.00 ms root dispersion: 26.50 ms peer dispersion: 10.00 ms reference time: 12:01:48.377 UTC Mar 2 2006(C7B15D2C.60A15981) synchronization state: clock synchronized
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # undo ntp-service server disable ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 cipher %#%#JA!v6M22=Gg\{>U.lx%#)c%yY}0*"/`5mi><QS)L%#%# ntp-service refclock-master 2 ntp-service authentication enable ntp-service server source-interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # undo ntp-service server disable ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 cipher %#%#>hD8))_H-XZVut2u3!_0lq3,+Ph=:OE}pX;T2M'9%#%# ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 ntp-service unicast-server 2.2.2.2 authentication-keyid 42 ntp-service authentication enable ntp-service server source-interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.11 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # undo ntp-service server disable ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 cipher %#%#m:fVJfk*r&3x"1J`21^K`Y;LH;B+g(t2<ZX^}Q_~%#%# ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 ntp-service unicast-server 10.0.0.1 authentication-keyid 42 ntp-service authentication enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # undo ntp-service server disable ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode hmac-sha256 cipher %#%#$\`_6BKWy1]kdR@=c;O@UX!)Vor5iYi|zIYEG_v5%#%# ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 ntp-service unicast-server 10.0.0.1 authentication-keyid 42 ntp-service authentication enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.0.3 255.255.255.0 # return