CUSP Fundamentals
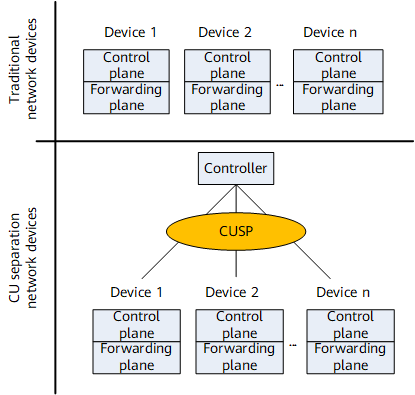
In Figure 1, each traditional network device consists of the control and forwarding planes. The devices independently process various types of packets through the two planes.
In a CU separation scenario, the user management functions of multiple BRAS devices are extracted and centralized to form a new control plane. Other control-plane functions and forwarding-plane functions on the BRAS devices are reserved to form a new forwarding plane for the devices. CUSP channels are used for the communications between the control and forwarding planes, so that the control plane delivers service entries to the forwarding plane and the forwarding plane reports service events to the control plane.
The controller uses Experimenter packets to deliver private flow tables to forwarders, implementing service entry delivery.
- Establishes a CUSP connection between the forwarder and controller.
- Reports local port information to the forwarder.
- Parses flow table information delivered by the controller.
- Transfers host packets related to the controller.