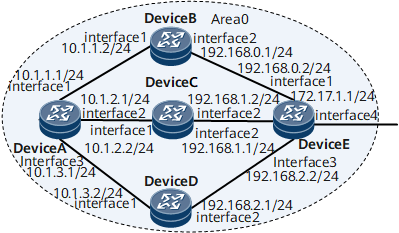
Example for Configuring OSPF Load Balancing
This section describes how to configure OSPF load balancing, including enabling load balancing and setting priorities for equal-cost routes.
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, the requirements are as follows:
Device A, Device B, Device C, Device D, and Device E are connected to each other through OSPF.
Device A, Device B, Device C, Device D, and Device E belong to Area 0.
Load balancing is configured so that the traffic from Device A to Device E is load-balanced by Device C and Device D.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic OSPF functions on each router for interconnection.
Configure load balancing on Device A.
Set the priority for equal-cost routes on Device A.
Configure per-packet load balancing on Device A.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data.
Data of DeviceA, including router ID (1.1.1.1), OSPF process ID (1), and network segment addresses of Area 0 (10.1.1.0/24, 10.1.2.0/24 and 10.1.3.0/24)
Data of DeviceB, including router ID (2.2.2.2), OSPF process ID (1), and network segment addresses of area 0 (10.1.1.0/24 and 192.168.0.0/24)
Data of DeviceC, including router ID (3.3.3.3), OSPF process ID (1), and network segment addresses of area 0 (10.1.2.0/24 and 192.168.1.0/24)
Data of DeviceD, including router ID (4.4.4.4), OSPF process ID (1), and network segment addresses of area 0 (10.1.3.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24)
Data of DeviceE, including router ID (5.5.5.5), OSPF process ID (1), and network segment addresses of area 0 (192.168.0.0/24, 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24, and 172.17.1.0/24)
Number of equal-cost routes for load balancing on Device A (2)
Next hop weights of the routes from Device A to Device B, Device C, and Device D (2, 1, and 1, respectively)
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic OSPF functions. For details, see Example for Configuring Basic OSPF Functions.
- Display the routing table of DeviceA.
As shown in the routing table, DeviceA has three valid next hops: DeviceB (10.1.1.2), DeviceC (10.1.2.2), and DeviceD (10.1.3.2) because the default maximum number of equal-cost routes is 64.
<DeviceA> display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Routing Table: _public_ Destinations : 15 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.2.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.3.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 10.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 10.1.3.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.0.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 192.168.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 192.168.2.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 172.17.1.0/24 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.3.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16
- Set the maximum number of routes for load balancing to 2 on Device A.
[~DeviceA] ospf 1 [*DeviceA-ospf-1] maximum load-balancing 2 [*DeviceA-ospf-1] commit [~DeviceA-ospf-1] quit
# Display the routing table of DeviceA. You can view two routes for load balancing on DeviceA, with DeviceB (10.1.1.2) and DeviceC (10.1.2.2) as the next hops.
[~DeviceA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Routing Table: _public_ Destinations : 15 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.2.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.3.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 10.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 10.1.3.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.0.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 192.168.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 192.168.2.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 172.17.1.0/24 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8
- Set the priority for equal-cost routes on Device A.
[~DeviceA] ospf 1 [*DeviceA-ospf-1] nexthop 10.1.1.2 weight 2 [*DeviceA-ospf-1] nexthop 10.1.2.2 weight 1 [*DeviceA-ospf-1] nexthop 10.1.3.2 weight 1 [*DeviceA-ospf-1] commit [*DeviceA-ospf-1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Display the routing table of Device A.
[~DeviceA] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Routing Table: _public_ Destinations : 15 Routes : 15 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 10.1.2.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.2.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 10.1.3.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 10.1.3.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 10.1.3.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 192.168.0.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 192.168.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 192.168.2.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16 172.17.1.0/24 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 OSPF 10 3 D 10.1.3.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/16
As shown in the routing table, the priority of the route with 10.1.2.2 and 10.1.3.2 as the next hop addresses is higher than that of the route with 10.1.1.2 as the next hop address. Therefore, Device A has only two valid next hops, Device C (10.1.2.2) and Device D (10.1.3.2).
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 maximum load-balancing 2 nexthop 10.1.1.2 weight 2 nexthop 10.1.2.2 weight 1 nexthop 10.1.3.2 weight 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device B configuration file
sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 router-id 4.4.4.4 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device E configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/24 undo shutdown ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.255.0 # ospf 1 router-id 5.5.5.5 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.17.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return